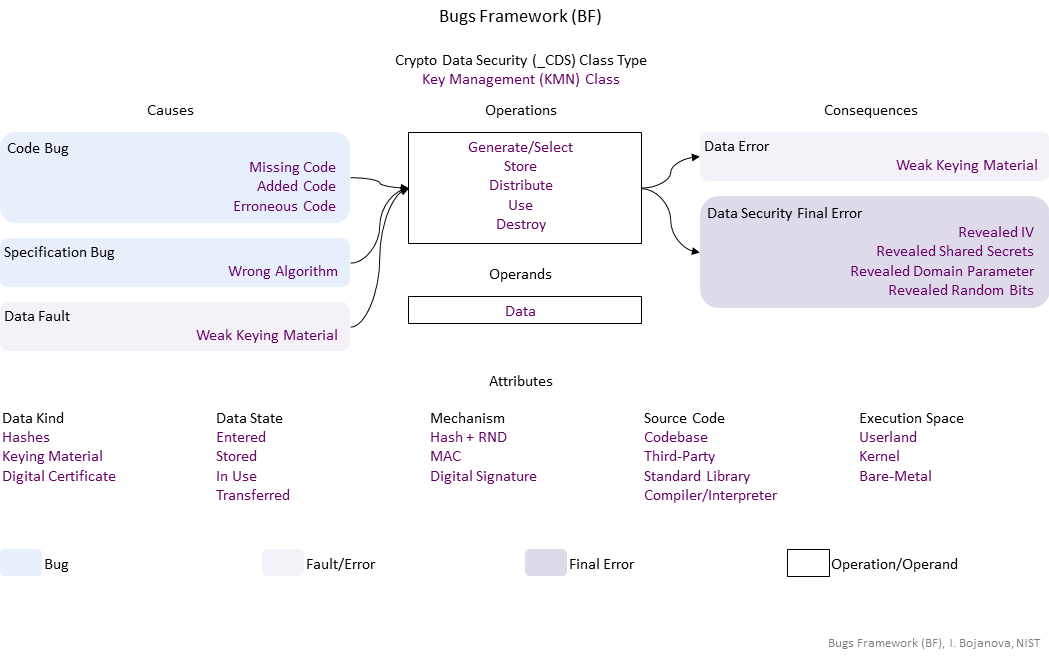
| Operations | Definition |
| Generate/Select | Generate/Select operation – yyyddd. |
| Store | Store operation – yyyddd. |
| Distribute | Distribute operation – yyyddd. |
| Use | Use operation – yyyddd. |
| Destroy | Destroy operation – yyyddd. |
| Operands | Definition |
| Data | Data operand – The data value of an object – stored in object's memory. |
| Causes | Definition |
| Code Bug | Code Bug Type – A code operation defect – proper operands over an improper operation. A first cause for the chain of weaknesses underlying a software security vulnerability. Must be fixed to resolve the vulnerability. |
| Missing Code | |
| Added Code | |
| Erroneous Code | |
| Specification Bug | Specification Bug Type – A specification operation defect – proper operands over an improper operation. A first cause for the chain of weaknesses underlying a software security vulnerability. Must be fixed to resolve the vulnerability. |
| Wrong Algorithm | |
| Data Fault | Data Fault/Error Type – The object data has harmed semantics or inconsistent or wrong value |
| Weak Keying Material | Weak Keying Material fault/error – yyyddd. |
| Consequences | Definition |
| Data Error | Data Fault/Error Type – The object data has harmed semantics or inconsistent or wrong value |
| Weak Keying Material | Weak Keying Material fault/error – yyyddd. |
| Data Security Final Error | Data Security exploitable error type – xxx |
| Revealed IV | Revealed IV exploitable error – A secret, public, or private key is exposed. |
| Revealed Shared Secrets | Revealed Shared Secrets exploitable error – A pre-master or other secret is exposed. |
| Revealed Domain Parameter | Revealed Domain Parameter exploitable error – A xxx is exposed. |
| Revealed Random Bits | Revealed Random Bits exploitable error – A random number (inlc. a salt or a nonce) is exposed. |
| Operations Attributes | Definition |
| Mechanism | Mechanism operation attribute type – Shows how the buggy/faulty operation code is performed. |
| Hash + RND | Hash + RND operation attribute – Hash Function + Random Numbers. |
| MAC | MAC operation attribute – Message Authentication Code. |
| Digital Signature | Digital Signature operation attribute – yyyddd. |
| Source Code | Source Code operation attribute type – Shows where the buggy/faulty operation code is in the program – in what kind of software. |
| Codebase | Codebase operation attribute – The operation is in the programmer's code - in the application itself. |
| Third-Party | Third-Party operation attribute – The operation is in a third-party software. |
| Standard Library | Standard Library operation attribute – The operation is in the standard library for a particular programming language. |
| Compiler/Interpreter | Compiler/Interpreter operation attribute – The operation is in the language processor that allows execution or creates executables (compiler, assembler, interpreter). |
| Execution Space | Execution Space operation attribute type – Shows where the buggy/faulty operation code is running or with what privilege level. |
| Userland | Userland operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with privilege levels, but in unprivileged mode (e.g., ring 3 in x86 architecture). |
| Kernel | Kernel operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with privilege levels with access privileged instructions (e.g., ring 0 in x86 architecture). |
| Bare-Metal | Bare-Metal operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment without privilege control. Usually, the program is the only software running and has total access to the hardware. |
| Operands Attributes | Definition |
| Data Kind | Data Kind operand attribute type – Shows what the data value is. |
| Hashes | Hashes operand attribute – Fixed-length bit strings mapped by a hash function from arbitrary length bit strings. They are used for integrity authentication. They are cryptographic data. |
| Keying Material | Keying Material operand attribute – Cryptographic keys (secret, public, private) and other crypto algorithm parameters (initialization vectors (IVs), shared secrets (e.g. pre-master secrets), domain parameters, and random bits (eandom number - RBG seeds, salt, nonce). |
| Digital Certificate | Digital Certificate operand attribute – yyyddd They are sensitive data. |
| Data State | Data State operand attribute type operand attribute – Shows where the data come from. |
| Entered | Entered operand attribute – The data are from a user via a user interface (e.g., input field of a dialog or a command prompt). |
| Stored | Stored operand attribute – The data are from a permanent storage (e.g., file, database on a storage device). |
| In Use | In Use operand attribute – The data are from a volatile storage (e.g., RAM, cache memory). |
| Transferred | Transferred operand attribute – The data are from another device via a network (e.g., connecting analog device or another computer). |