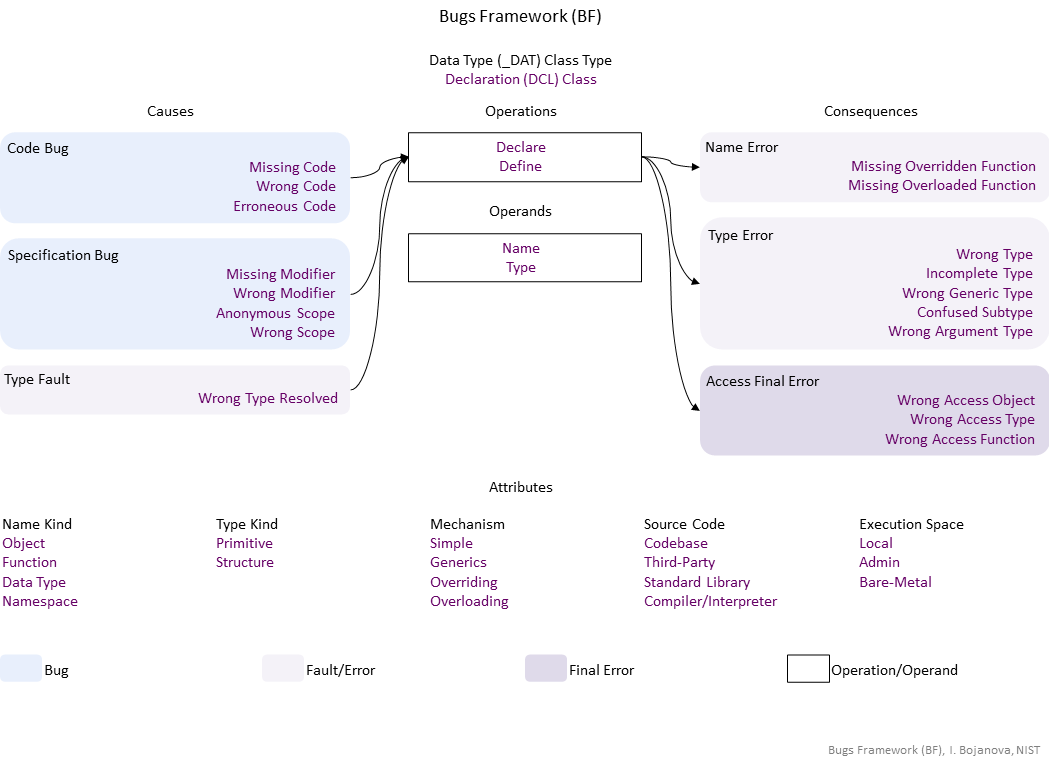
| Operations | Definition |
| Declare | Declare operation – Specify the name and type of an object; the name, return type, and parameters of a function; or the name and type parameters of a type. |
| Define | Define operation – Specify the implementation of a function; or the member objects and functions of a type. (The data of an object is specified at its initialization – see MAD and MUS.) |
| Operands | Definition |
| Name | Name operand – The identifier of an object, function, or data type entity used to reference it. |
| Type | Type operand – The data type of an object – i.e., the set of allowed values (e.g., char is within [-128, 127]) and operations over them (e.g., +, *, mod). |
| Size | Size operand – The memory size of an object – the number of bytes allocated for an object in memory. Its value is contained by (is data of) of another object. |
| Causes | Definition |
| Code Bug | Code Bug type – An error in the implementation of an operation – proper operands over an improper operation. A first cause for the chain of weaknesses underlying a software security vulnerability. Must be fixed to resolve the vulnerability. |
| Missing Code | Missing Code bug - The operation is entirely absent. |
| Wrong Code | Wrong Code bug - An incorrect operator or function is used, or an incorrect data type is specified. |
| Erroneous Code | Erroneous Code bug - There is a coding error in the implementation of the operation. |
| Specification Bug | Specification Bug type – A defect in the metadata or algorithm of an operation – proper operands over an improper operation. It is always the first cause for the chain of weaknesses underlying a software security vulnerability. It must be fixed to resolve the vulnerability. |
| Missing Modifier | A required behavioral restriction is absent. |
| Wrong Modifier | A wrong behavioral restriction is specified. |
| Anonymous Scope | The declaration is in an unnamed scope. |
| Wrong Scope | |
| Data Fault | Data Fault/Error type – The data of an object has harmed semantics or inconsistent or wrong value. |
| Wrong Name | Wrong Name fault/error – Inaccurate name is constructed dynamically for use at run time. |
| Type Fault | Type Fault/Error type – The set or range of allowed values of an entity is wrong or the operations allowed on them are wrong. |
| Wrong Type Resolved | Wrong Type Resolved fault/error – A data type is resolved from a wrong scope. |
| Consequences | Definition |
| Name Error | Name Fault/Error type – The fully resolved name of an entity is wrong. |
| Missing Overridden Function | Missing Overridden Function fault/error – The function implementation in a particular subclass is absent. |
| Missing Overloaded Function | Missing Overloaded Function fault/error – Code for particular function parameters' data types is absent. |
| Type Error | Type Fault/Error type – The set or range of allowed values of an entity is wrong or the operations allowed on them are wrong. |
| Wrong Type | Wrong Type fault/error – A data type range or structure is not correct. |
| Incomplete Type | Incomplete Type fault/error – A specific constructor, method, or overloaded function is missing. |
| Wrong Generic Type | Wrong Generic Type fault/error – A generic object is instantiated via wrong type argument. |
| Wrong Argument Type | Wrong Argument Type fault/error – An argument to an overloaded function is of incorrect data type. |
| Size Error | Type Fault/Error type – The set or range of allowed values of an entity is wrong or the operations allowed on them are wrong. |
| Insufficient Size | Insufficient Size fault/error – The allocated memory is too little for the data it should store. |
| Entity Access Final Error | Entity Access final error type – An exploitable or undefined system behavior caused by declaration bugs. |
| Wrong Access Object | Wrong Access Object final error – An unauthorized access to an object; allows access to sensitive data or to member functions. |
| Wrong Access Type | Wrong Access Type final error – An unauthorized access to a data type; allows access to member objects and functions. |
| Wrong Access Function | Wrong Access Function final error – An unauthorized access to a function; allows its execution. |
| Operations Attributes | Definition |
| Mechanism | Mechanism operation attribute type – Shows how the operation the operation with a bug or faulty operand is performed. |
| Simple | Simple operation attribute – The operation is via non-polymorphic types. |
| Generics | Generics operation attribute – The operation is via parameterization by types. |
| Overriding | Overriding operation attribute – The operation is via functions with the same name as one in the base type but implemented in different subtypes. |
| Overloading | Overloading operation attribute – The operation is via functions with the same name in the same declaration scope, but implemented with different signature. |
| Source Code | Source Code operation attribute type – Shows where the code of the operation with a bug or faulty operand resides within the software, firmware, or hardware. |
| Codebase | Codebase operation attribute – The operation is in the programmer's code - in the application itself. |
| Third-Party | Third-Party operation attribute – The operation code is in a third-party source. |
| Standard Library | Standard Library operation attribute – The operation code is in the standard library for a particular programming language. |
| Compiler/Interpreter | Compiler/Interpreter operation attribute – The operation code is in the language processor that allows execution or creates executables (interpreter, compiler, assembler). |
| Execution Space | Execution Space operation attribute type – Shows where the operation with a bug or faulty operand is executed and the privilege level at which it runs. |
| Local | Local operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with access control policy with limited (local user) permission. |
| Admin | Admin operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with access control policy with unlimited (admin user) permission. |
| Bare-Metal | Bare-Metal operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment without privilege control. Usually, the program is the only software running and has total access to the hardware. |
| Operands Attributes | Definition |
| Name Kind | Name Kind operand attribute type – Shows what the entity with this name is. |
| Object | Object operand attribute – A memory region used to store data. |
| Function | Function operand attribute – An organized block of code that when called takes in data, processes it, and produces a result(s). |
| Data Type | Data Type operand attribute – A set of allowed values and the operations allowed over them. |
| Namespace | Namespace operand attribute – An organization of entities' names, utilized to avoid names collision. |
| Type Kind | Type Kind operand attribute type – Shows what the data type composition is. |
| Primitive | Primitive operand attribute – A scalar data type that mimics the hardware units - e.g., int (long, short, signed), float, double, string, Boolean. A primitive data type is only language defined and is not built from other data types. |
| Structure | Structure operand attribute – A composite data type - e.g., array, list, map, class. A structured data type is built from other data types and has primitive or structured members. |
| Size Kind | Size Kind operand attribute type – Shows what is used as the size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of an object - e.g., as the limit for traversal over the elements. |
| Actual | Actual operand attribute – The real size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of the allocated memory for an object. |
| Used | Used operand attribute – A supplied value to be used as the size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of an object. |