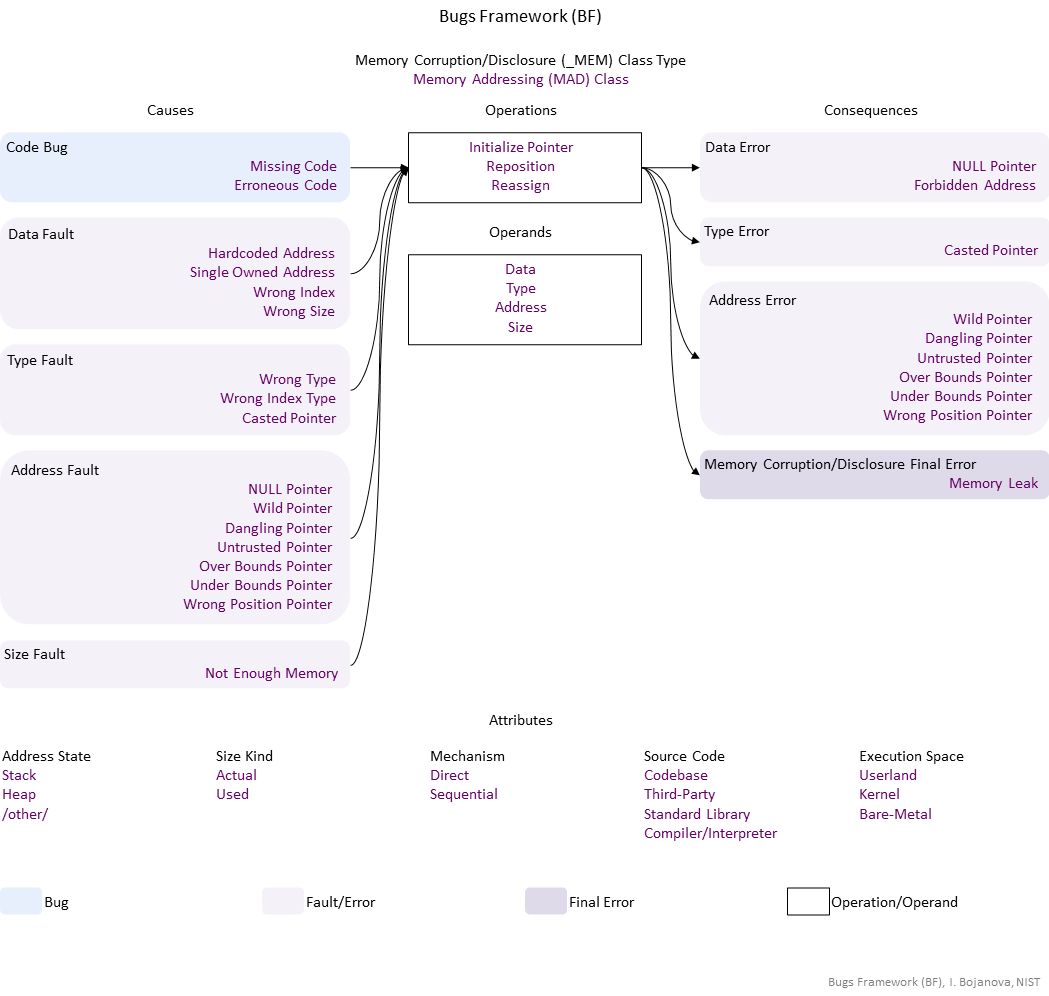
| Operations | Definition |
| Initialize Pointer | Initialize Pointer operation – Change the undefined data value of a pointer to a meaningful object address; and position the pointer at the start of the object. |
| Dereference | Dereference operation – Interpret a pointer value as memory address and access that memory location. The pointer datatype determines the data type of the values to be read or written. |
| Reposition | Reposition operation – Change the pointer to another position inside its object. |
| Reassign | Reassign operation – Direct the pointer to a different object. |
| Operands | Definition |
| Data | Data operand – The data value of an object – i.e., the actual value that is stored in memory. |
| Address | Address operand attribute – The memory address for an object. Its value is data of another object -- the object's pointer, used to reference and traverse it. |
| Size | Size operand – The memory size of an object – the number of bytes allocated for an object in memory. Its value is contained by (is data of) of another object. |
| Causes | Definition |
| Code Bug | Code Bug type – An error in the implementation of an operation – proper operands over an improper operation. A first cause for the chain of weaknesses underlying a software security vulnerability. Must be fixed to resolve the vulnerability. |
| Missing Code | Missing Code bug - The operation is entirely absent. |
| Erroneous Code | Erroneous Code bug - There is a coding error in the implementation of the operation. |
| Data Fault | Data Fault/Error type – The data of an object has harmed semantics or inconsistent or wrong value. |
| NULL Pointer | NULL Pointer fault/error – The pointer does not point to a valid object; usually holds the zero memory address. |
| Hardcoded Address | Hardcoded Address fault/error – The pointer holds a wrong specific address. |
| Single Owned Address | Single Owned Address fault/error – Exactly one pointer owns the object. |
| Wrong Index | Wrong Index fault/error – Incorrect index position – hardcoded or from computation. |
| Wrong Size | Wrong Size fault/error – The value used as size or length (i.e., the number of elements) does not match an object's memory size or length (e.g., to limit a pointer reposition or index increment/decrement in a repetition statement). |
| Type Fault | Type Fault/Error type – The set or range of allowed values of an entity is wrong or the operations allowed on them are wrong. |
| Cast Pointer | Cast Pointer fault/error – A pointer is type cast to a data type that is incompatible with its object's data type. |
| Wrong Type | Wrong Type fault/error – A data type range or structure is not correct. |
| Wrong Index Type | Wrong Index Type fault/error – An index is of incorrect data type. |
| Address Fault | Address Fault/Error type – The address of an object is wrong. |
| Wild Pointer | Wild Pointer fault/error – Holds an arbitrary address, because it has not been initialized or an erroneous allocation routine is used. |
| Dangling Pointer | Dangling Pointer fault/error – Still holds the address of its successfully deallocated object (e.g., a pointer to a freed heap object or address of a stack object returned by a function). |
| Untrusted Pointer | Untrusted Pointer fault/error – The pointer is modified to an improperly checked address. |
| Overbound Pointer | Overbound Pointer fault/error – Holds an address that is above the upper boundary of its object. |
| Underbound Pointer | Underbound Pointer fault/error – Holds an address that is below the lower boundary of its object. |
| Wrong Position Pointer | Wrong Position Pointer fault/error – Holds the address of a miscalculated position inside its object bounds. |
| Size Fault | Type Fault/Error type – The set or range of allowed values of an entity is wrong or the operations allowed on them are wrong. |
| Insufficient Size | Insufficient Size fault/error – The allocated memory is too little for the data it should store. |
| Consequences | Definition |
| Data Error | Data Fault/Error type – The data of an object has harmed semantics or inconsistent or wrong value. |
| NULL Pointer | NULL Pointer fault/error – The pointer does not point to a valid object; usually holds the zero memory address. |
| Forbidden Address | Forbidden Address fault/error – The pointer holds an OS protected address or a non-existing address. |
| Address Error | Address Fault/Error type – The address of an object is wrong. |
| Wild Pointer | Wild Pointer fault/error – Holds an arbitrary address, because it has not been initialized or an erroneous allocation routine is used. |
| Dangling Pointer | Dangling Pointer fault/error – Still holds the address of its successfully deallocated object (e.g., a pointer to a freed heap object or address of a stack object returned by a function). |
| Untrusted Pointer | Untrusted Pointer fault/error – The pointer is modified to an improperly checked address. |
| Overbound Pointer | Overbound Pointer fault/error – Holds an address that is above the upper boundary of its object. |
| Underbound Pointer | Underbound Pointer fault/error – Holds an address that is below the lower boundary of its object. |
| Wrong Position Pointer | Wrong Position Pointer fault/error – Holds the address of a miscalculated position inside its object bounds. |
| Memory Corruption/Disclosure Final Error | Memory Corruption/Disclosure final error type – An exploitable or undefined system behavior caused by memory addressing, allocation, use, or deallocation bugs. |
| NULL Pointer Dereference | NULL Pointer Dereference final error – An attempt to access an object for reading or writing via a NULL pointer. |
| Untrusted Pointer Dereference | Untrusted Pointer Dereference final error – An attempt to access an object via an altered pointer (not legitimate dereference of a tainted pointer). |
| Uninitialized Pointer Dereference | Uninitialized Pointer Dereference final error – An attempt to access an object for reading or writing via an uninitialized pointer. |
| Memory Leak | Memory Leak final error – An object has no pointer pointing to it. |
| Operations Attributes | Definition |
| Mechanism | Mechanism operation attribute type – Shows how the operation the operation with a bug or faulty operand is performed. |
| Direct | Direct operation attribute – The operation is on a particular object element. |
| Sequential | Sequential operation attribute – The operation is via iterating over the object elements. |
| Source Code | Source Code operation attribute type – Shows where the code of the operation with a bug or faulty operand resides within the software, firmware, or hardware. |
| Codebase | Codebase operation attribute – The operation is in the programmer's code - in the application itself. |
| Third-Party | Third-Party operation attribute – The operation code is in a third-party source. |
| Standard Library | Standard Library operation attribute – The operation code is in the standard library for a particular programming language. |
| Compiler/Interpreter | Compiler/Interpreter operation attribute – The operation code is in the language processor that allows execution or creates executables (interpreter, compiler, assembler). |
| Execution Space | Execution Space operation attribute type – Shows where the operation with a bug or faulty operand is executed and the privilege level at which it runs. |
| Userland | Userland operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with privilege levels, but in unprivileged mode (e.g., ring 3 in x86 architecture). |
| Kernel | Kernel operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with privilege levels with access privileged instructions (e.g., ring 0 in x86 architecture). |
| Bare-Metal | Bare-Metal operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment without privilege control. Usually, the program is the only software running and has total access to the hardware. |
| Operands Attributes | Definition |
| Address State | Address State operand attribute type – Shows where the address is (i.e., its location) in the memory layout. |
| Stack | |
| Heap | |
| /other/ | |
| Size Kind | Size Kind operand attribute type – Shows what is used as the size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of an object - e.g., as the limit for traversal over the elements. |
| Actual | Actual operand attribute – The real size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of the allocated memory for an object. |
| Used | Used operand attribute – A supplied value to be used as the size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of an object. |