BF Specification of CVE-2004-1287 Stack Buffer Overflow in NASM 0.98.38 1.2
-0.png)
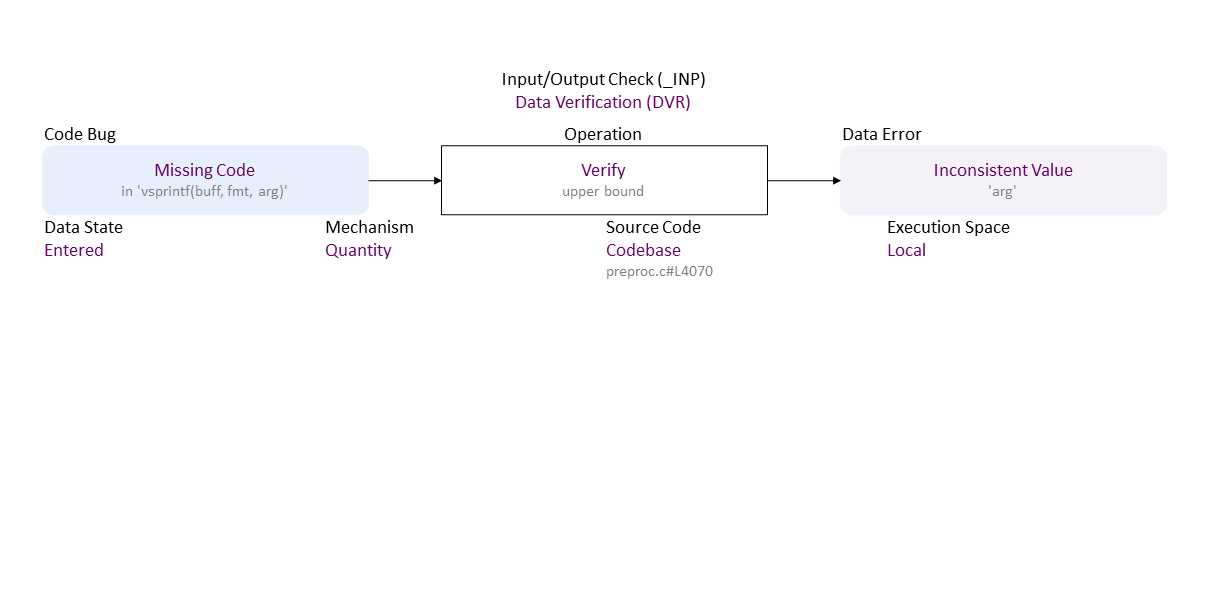
Missing verification of 'arg' towards a upper limit leads to use of an inconsistent size for an object, allowing a pointer reposition over its bounds, which, when used in ‘vsprintf()' leads to a stack buffer overflow. If exploited, this can lead to data tampering, denial of service (application crash), or remote code execution.
//generated// Missing Code (in ‘vsprintf(buff, fmt, arg)’) to Quantity Verify upper bound Entered in Codebase (preproc.c#L4070) Local leads to Inconsistent Value (‘arg’)
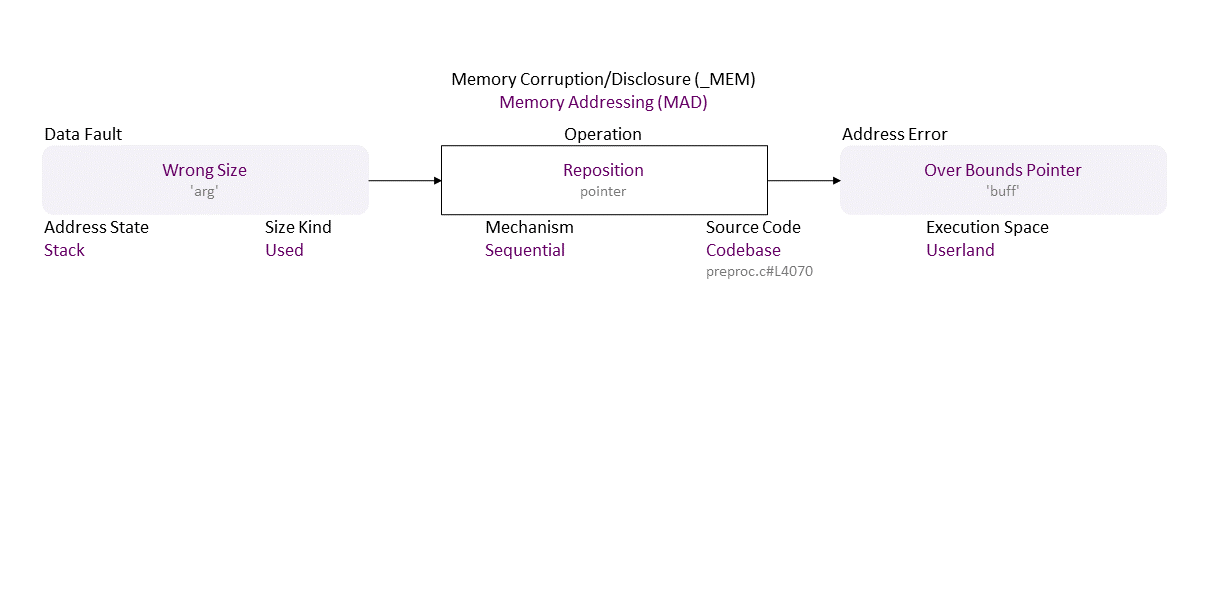
, which propagates to Wrong Size (‘arg’) Sequential Reposition (pointer) Stack Used Codebase (preproc.c#L4070) in Userland resulting in Overbound Pointer (‘buff’)
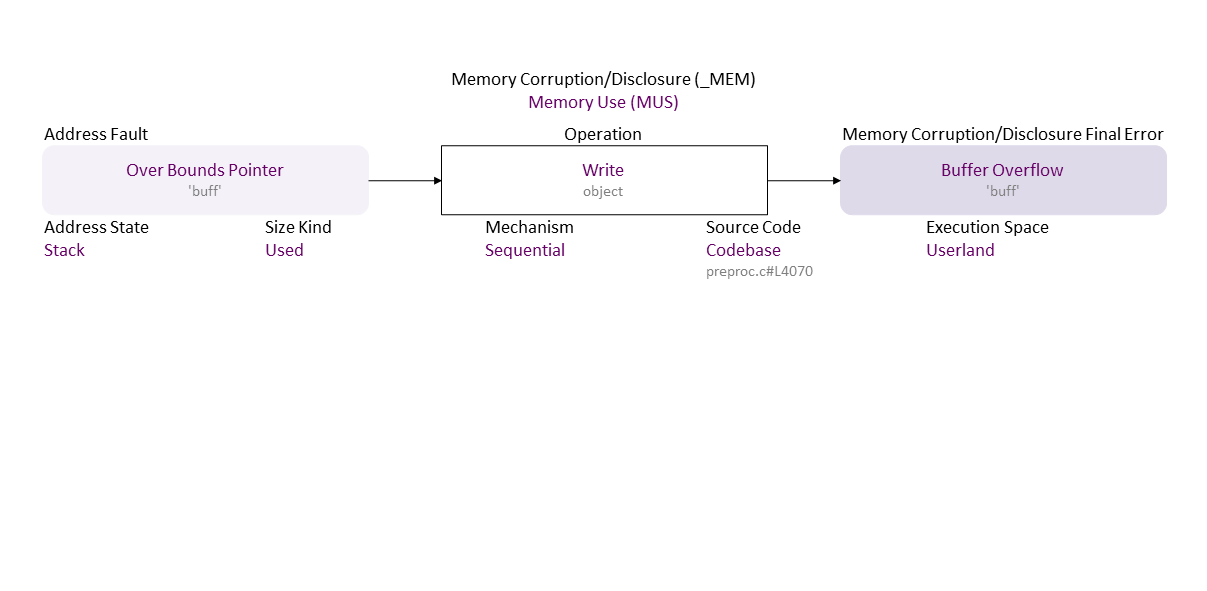
, which propagates to Overbound Pointer (‘buff’) Sequential Write (object) Stack Used Codebase (preproc.c#L4070) in Userland resulting in Buffer Overflow (‘buff’)
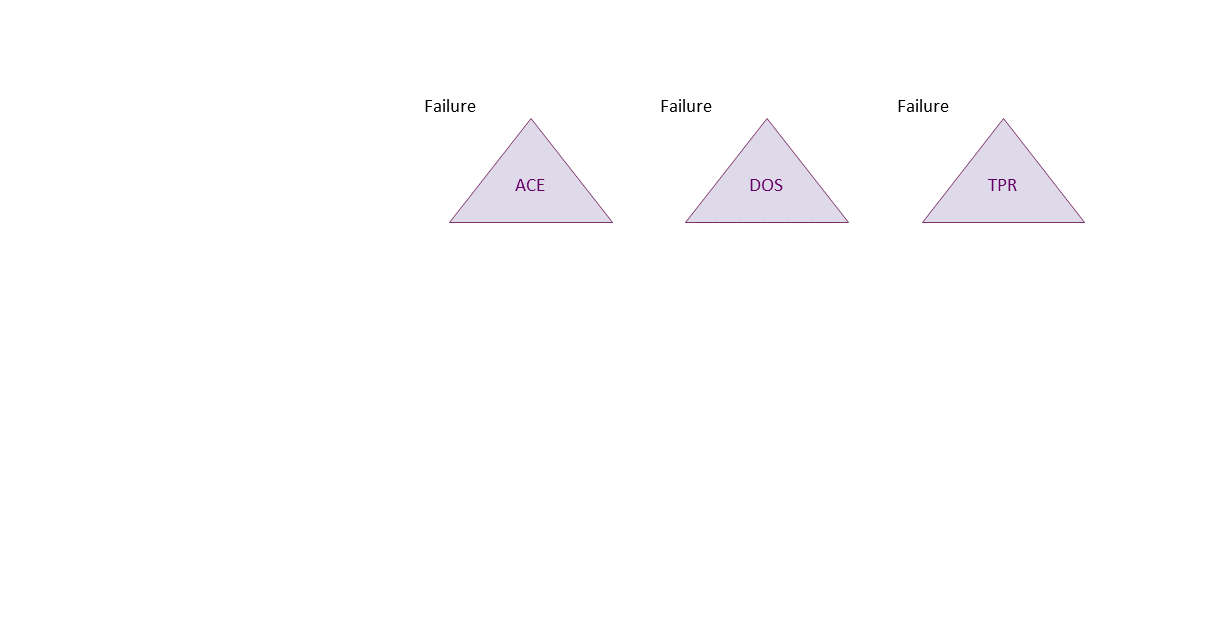
. If exploited this can lead to ACE (everything could be lost) or DOS (availability loss) or TPR (integrity loss).
|
|
| Class | Definition |
| DVR | Data Verification (DVR) class – Data are verified (i.e., semantics check) or corrected (i.e., assign or remove) improperly. |
| MAD | Memory Addressing (MAD) class – The pointer to an object is initialized, dereferenced, repositioned, or reassigned to an improper memory address. |
| MUS | Memory Use (MUS) class – An object is initialized, read, written, or cleared improperly. |
| Operation | Definition |
| Verify | Verify operation – Check data semantics (e.g., proper value/meaning) in order to accept (and possibly correct) or reject it. |
| Reposition | Reposition operation – Change the pointer to another position inside its object. |
| Write | Write operation – Change the data value of an object in memory to another meaningful value. |
| Cause/Consequence | Definition |
| Code Bug | Code Bug type – An error in the implementation of an operation – proper operands over an improper operation. It is the roor cause of a security vulnerability. Must be fixed to resolve the vulnerability. |
| Missing Code | Missing Code bug - The operation is misplaced entirely absent. |
| Data Error/Fault | Data Fault/Error type – The data of an object has harmed semantics or inconsistent or wrong value. |
| Inconsistent Value | Inconsistent Value fault/error – The data value does not correspond to related data value (e.g., inconstancy between the value of a size variable and the actual buffer size). |
| Wrong Size | Wrong Size fault/error – The value used as size or length (i.e., the number of elements) does not match the object's memory size or length (e.g., to limit a pointer reposition or index increment/decrement in a repetition statement). |
| Address Error/Fault | Address Fault/Error type – The address of an object is wrong. |
| Overbound Pointer | Overbound Pointer fault/error – Holds an address that is above the upper boundary of its object. |
| Memory Corruption/Disclosure Final Error | Memory Corruption/Disclosure enabler/final error type – An exploitable or undefined system behavior caused by memory addressing, allocation, use, or deallocation bugs. |
| Buffer Overflow | Buffer Overflow final error – Write data above the upper bound of an object (i.e., buffer overwrite). |
| Operation Attribute | Definition |
| Mechanism | Mechanism operation attribute type – Shows how the operation the operation with a bug or faulty operand is performed. |
| Quantity | Quantity operation attribute – The operation checks data for a specific measurable value (e.g., size, time, rate, frequency). |
| Sequential | Sequential operation attribute – The operation is via iterating over the object elements. |
| Source Code | Source Code operation attribute type – Shows where the code of the operation with a bug or faulty operand resides within the software, firmware, or hardware. |
| Codebase | Codebase operation attribute – The operation is in the programmer's code - in the application itself. |
| Execution Space | Execution Space operation attribute type – Shows where the operation with a bug or faulty operand is executed and the privilege level at which it runs. |
| Local | Local operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with access control policy with limited (local user) permission. |
| Userland | Userland operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with privilege levels, but in unprivileged mode (e.g., ring 3 in x86 architecture). |
| Operand Attribute | Definition |
| Data State | Data State operand attribute type – Shows where the data comes from. |
| Entered | Entered operand attribute – Data are from a user via a user interface (e.g., input field of a dialog or a command prompt). |
| Address State | Address State operand attribute type – Shows where the address is (i.e., its location) in the memory layout. |
| Stack | The object is a non-static local variable (defined in a function, a passed parameter, or a function return address). |
| Size Kind | Size Kind operand attribute type – Shows what is used as the size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of an object - e.g., as the limit for traversal over the elements. |
| Used | Used operand attribute – A supplied value to be used as the size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of an object. |