BF Specification of CVE-2013-4930 Wireshark v1.8.x before v1.8.9 and v1.10.x before v1.10.1 (trace from SARD-231364)
-0.png)
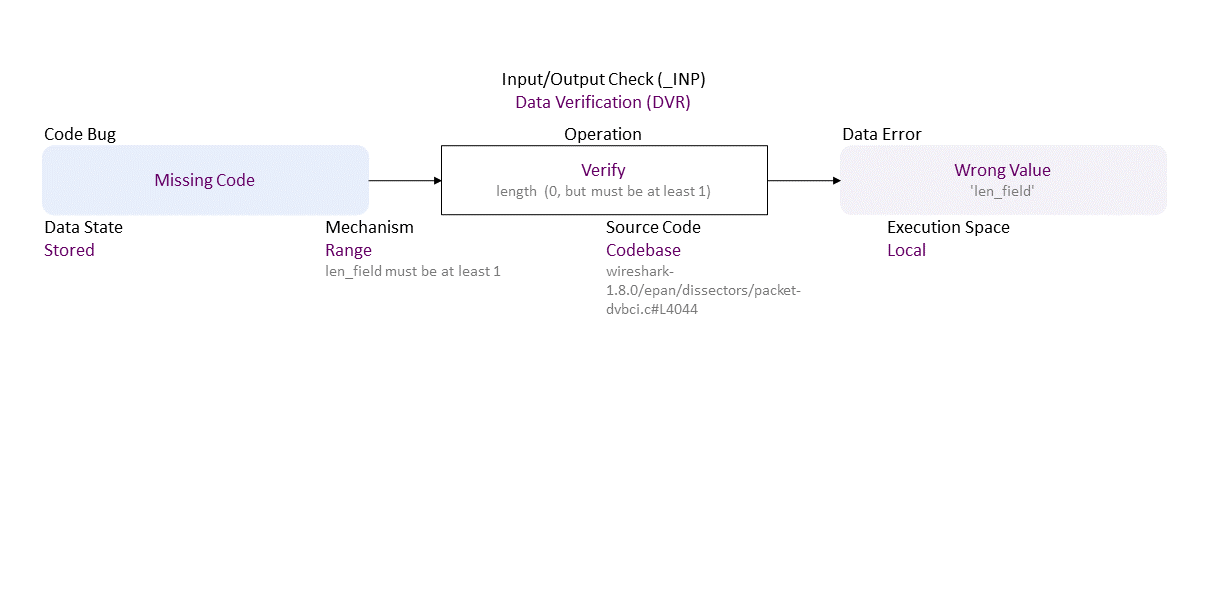
//generated// Missing Code to Range Verify length (0, but must be at least 1) (len_field must be at least 1) Stored in Codebase (wireshark-1.8.0/epan/dissectors/packet-dvbci.c#L4044) Local leads to Wrong Value (’len_field')
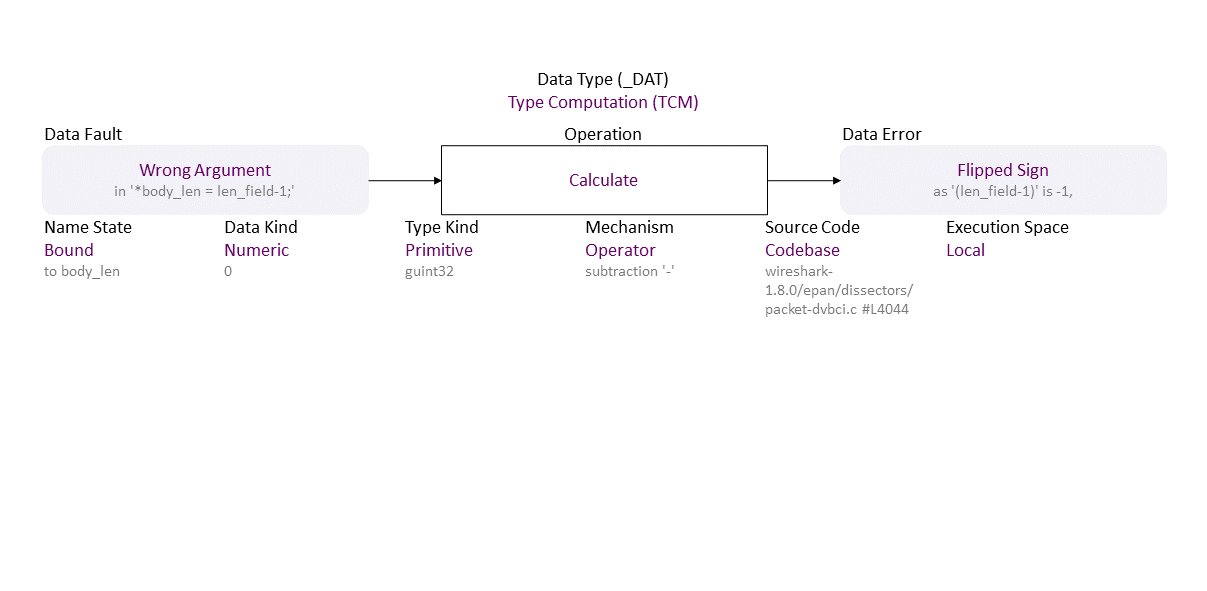
, which propagates to Wrong Argument (in ‘*body_len = len_field-1;’) Operator Calculate (subtraction ‘-’) Bound (to body_len) Numeric (0) Primitive (guint32) Codebase (wireshark-1.8.0/epan/dissectors/packet-dvbci.c #L4044) in Local resulting in Flipped Sign (as ‘(len_field-1)’ is -1,)
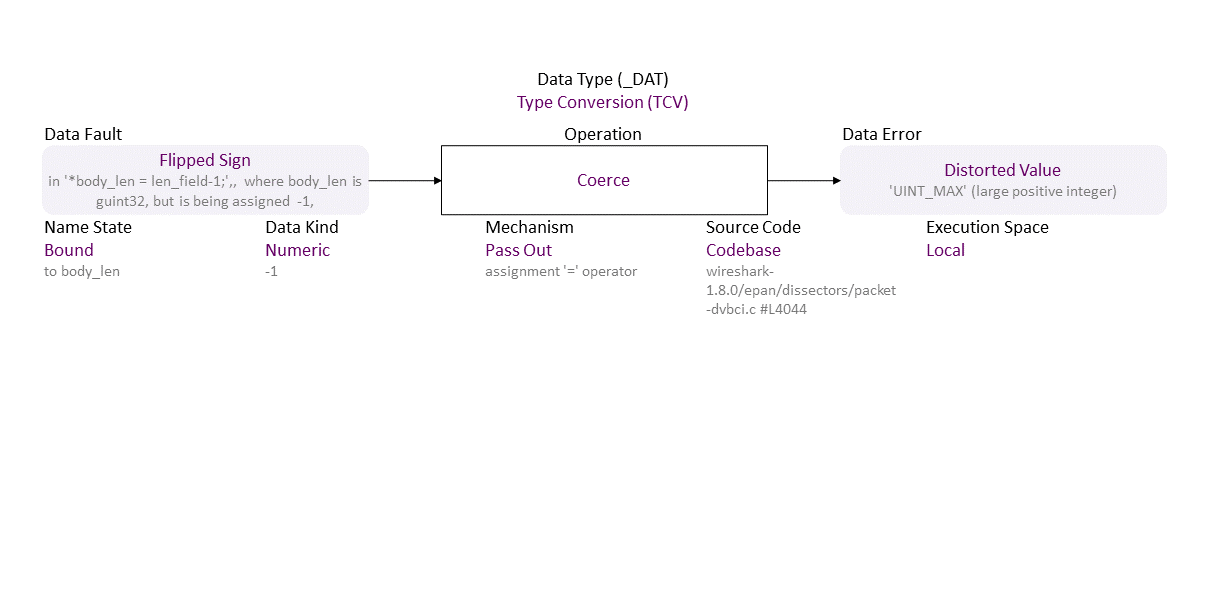
, which propagates to Flipped Sign (in ‘*body_len = len_field-1;’,, where body_len is guint32, but is being assigned -1,) Pass Out Coerce (assignment ‘=’ operator) Bound (to body_len) Numeric (-1) Codebase (wireshark-1.8.0/epan/dissectors/packet-dvbci.c #L4044) in Local resulting in Distorted Value (‘UINT_MAX’ (large positive integer))
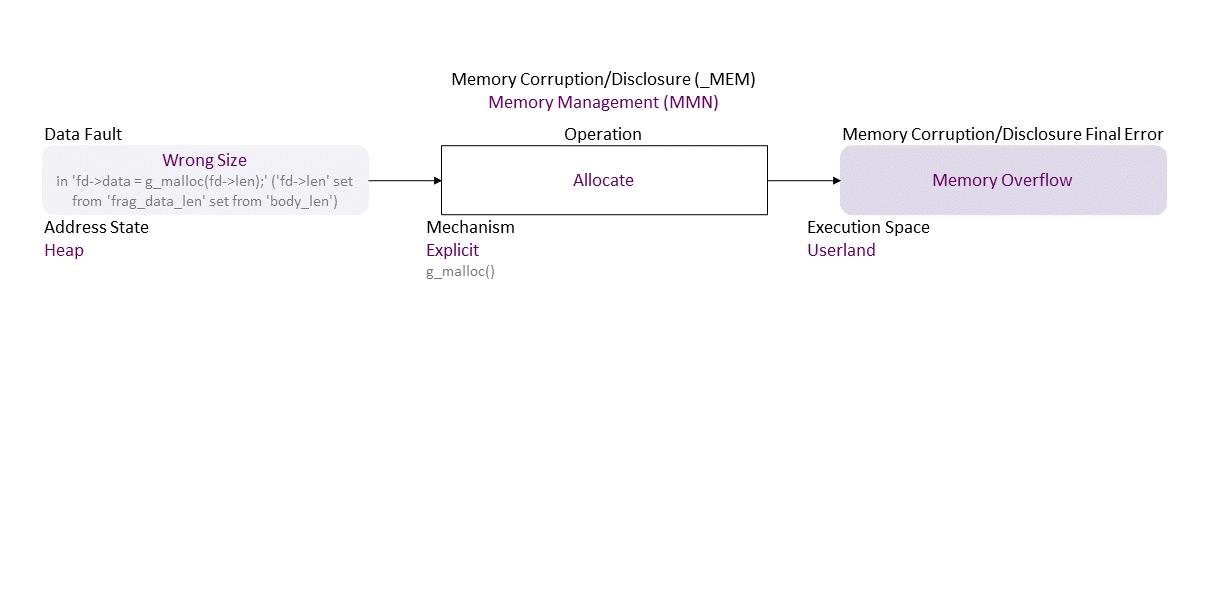
, which propagates to Wrong Size (in ‘fd->data = g_malloc(fd->len);’ (‘fd->len’ set from ‘frag_data_len’ set from ‘body_len’)) Explicit Allocate (g_malloc()) Heap Userland in resulting in Memory Overflow
. If exploited this can lead to DOS (assertion failure and application exit) (availability loss).
vendor:product: wireshark:wireshark:1.8.0 |
| Class | Definition |
| DVR | Data Verification (DVR) class – Data are verified (semantics check) or corrected (assign, remove) improperly. |
| TCM | Type Computation (TCM) class – An arithmetic expression (over numbers, strings, or pointers) is calculated improperly, or a boolean condition is evaluated improperly. |
| TCV | Type Conversion (TCV) class – Data are converted or coerced into other type improperly. |
| MMN | Memory Management (MMN) class – An object is allocated, deallocated, or resized improperly. |
| Operation | Definition |
| Verify | Verify operation – Check data semantics (proper value/meaning) in order to accept (and possibly correct) or reject it. |
| Calculate | Calculate operation – Find the result of a numeric, pointer, or string operation. |
| Coerce | Coerce operation – Implicitly (forced by the Type System) convert the value of a passed in/out argument or the return into the corresponding parameter or return data type. (Type Coercion is known also as Type Juggling.) |
| Allocate | Allocate operation – Reserve space in memory for an object; defines its initial boundaries and size. |
| Cause/Consequence | Definition |
| Code Bug | Code Bug type – Defect in the implementation of the operation – proper operands over an improper operation. A first cause for the chain of weaknesses underlying a software security vulnerability. Must be fixed to resolve the vulnerability. |
| Missing Code | Missing Code bug - The operation is entirely absent. |
| Data Error/Fault | Data Fault/Error type – The object data has harmed semantics or inconsistent or wrong value. |
| Wrong Value | Wrong Value fault/error – The value of the data is not accurate (e.g., outside of a range). |
| Wrong Argument | Wrong Argument fault/error – Inaccurate input data value, i.e., non-verified for harmed semantics. |
| Flipped Sign | Flipped Sign fault/error – Sign bit is overwritten from type related calculation. |
| Distorted Value | Distorted Value fault/error – Incorrect value (although fits type size) due to sign flip or signed/unsigned and vice versa cast. |
| Wrong Size | Wrong Size fault/error – The value used as size does not match the actual size of the object (e.g., to restrict pointer repositioning or index increment/decrement in a repetition statement). |
| Memory Corruption/Disclosure Final Error | Memory Corruption/Disclosure exploitable error type – An exploitable or undefined system behavior caused by memory addressing, allocation, use, and deallocation bugs. |
| Memory Overflow | Memory Overflow exploitable error – More memory is requested than available. |
| Operation Attribute | Definition |
| Mechanism | Mechanism operation attribute type – Shows how the buggy/faulty operation code is performed. |
| Range | Range operation attribute – The operation checks data are within a (min, max) interval. |
| Operator | Operator operation attribute – The operation is via a function with a symbolic name that implements a mathematical, relational or logical operation. |
| Pass Out | Pass Out operation attribute – The operation is via "out" or "in/out" arguments' values or a return value to a function/ operator. |
| Explicit | Explicit operation attribute – The operation is via a function/method call. |
| Source Code | Source Code operation attribute type – Shows where the operation with the bug or a faulty operand is in the program – in what kind of software. |
| Codebase | Codebase operation attribute – The operation is in the programmer's code - in the application itself. |
| Execution Space | Execution Space operation attribute type – Shows where the buggy/faulty operation code is running or with what privilege level. |
| Local | Local operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with access control policy with limited (local user) permission. |
| Userland | Userland operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with privilege levels, but in unprivileged mode (e.g., ring 3 in x86 architecture). |
| Operand Attribute | Definition |
| Data State | Data State operand attribute type operand attribute – Shows where the data come from. |
| Stored | Stored operand attribute – Data are from a permanent storage (e.g., file, database on a storage device); they are at rest. |
| Name State | Name State operand attribute type – Shows at what stage the entity name is. |
| Bound | Bound operand attribute – The name is linked to a declared (or inferred) data type, a defined object's data, or a called function implementation. |
| Data Kind | Data Kind operand attribute type – Shows what the data value is. |
| Numeric | Numeric operand attribute – A number – a sequence of digits. |
| Type Kind | Type Kind operand attribute type – Shows what the data type composition is. |
| Primitive | Primitive operand attribute – A scalar data type that mimics the hardware units - e.g., int (long, short, signed), float, double, string, Boolean. A primitive data type is only language defined and is not built from other data types. |
| Address State | Address State operand attribute type - State operand attribute type – Shows where the address is in the memory layout. |
| Heap | Heap operand attribute – The object is a dynamically allocated data structure (e.g., via malloc() and new). |