BF Specification of CVE-2015-0235 GHOST in GNU glibc v2.2, and other v2.x before v2.18
-0.png)
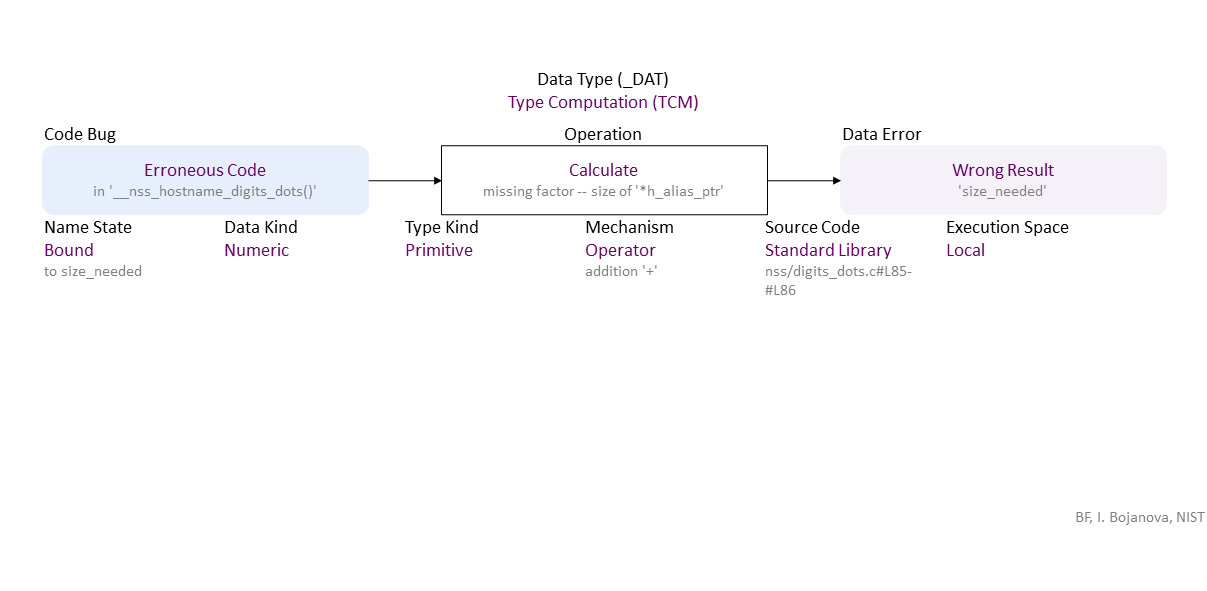
//generated// Erroneous Code (in ‘__nss_hostname_digits_dots()’) to Operator Calculate missing factor – size of ‘*h_alias_ptr’ (addition ‘+’) Bound (to size_needed) Numeric Primitive in Standard Library (nss/digits_dots.c#L85-#L86) Local leads to Wrong Result (‘size_needed’)
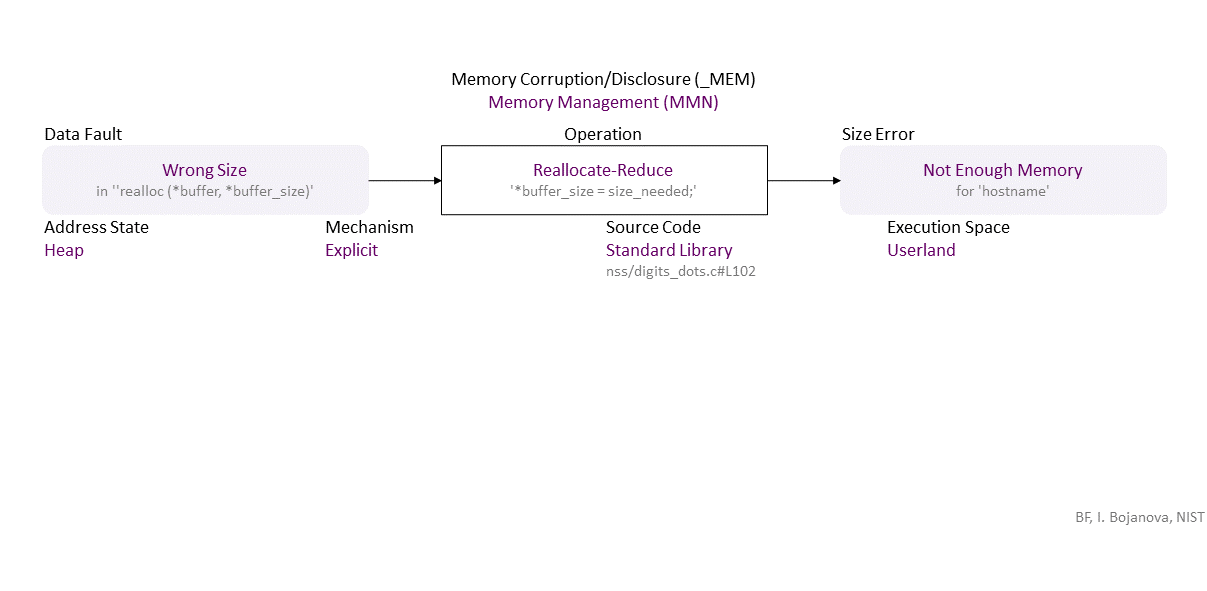
, which propagates to Wrong Size (in ‘‘realloc (*buffer, *buffer_size)’) Explicit Reallocate-Reduce (’*buffer_size = size_needed;’) Heap Standard Library (nss/digits_dots.c#L102) in Userland that results in Not Enough Memory (for ‘hostname’)
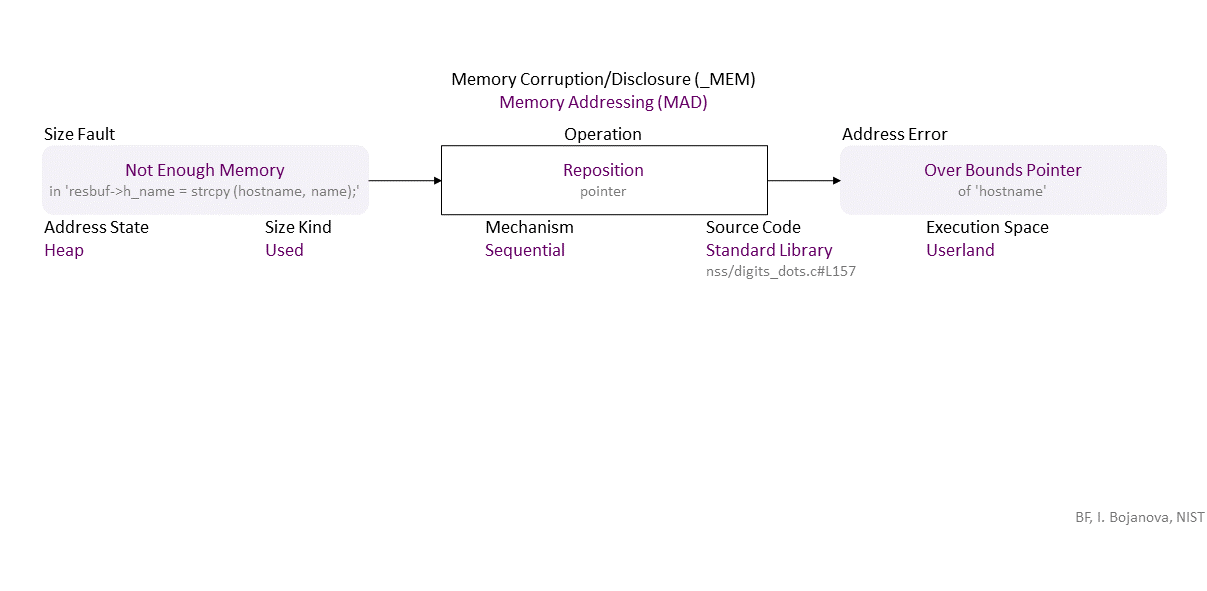
, which propagates to Not Enough Memory (in ‘resbuf->h_name = strcpy (hostname, name);’) Sequential Reposition (pointer) Heap Used Standard Library (nss/digits_dots.c#L157) in Userland that results in Overbound Pointer (of ‘hostname’)
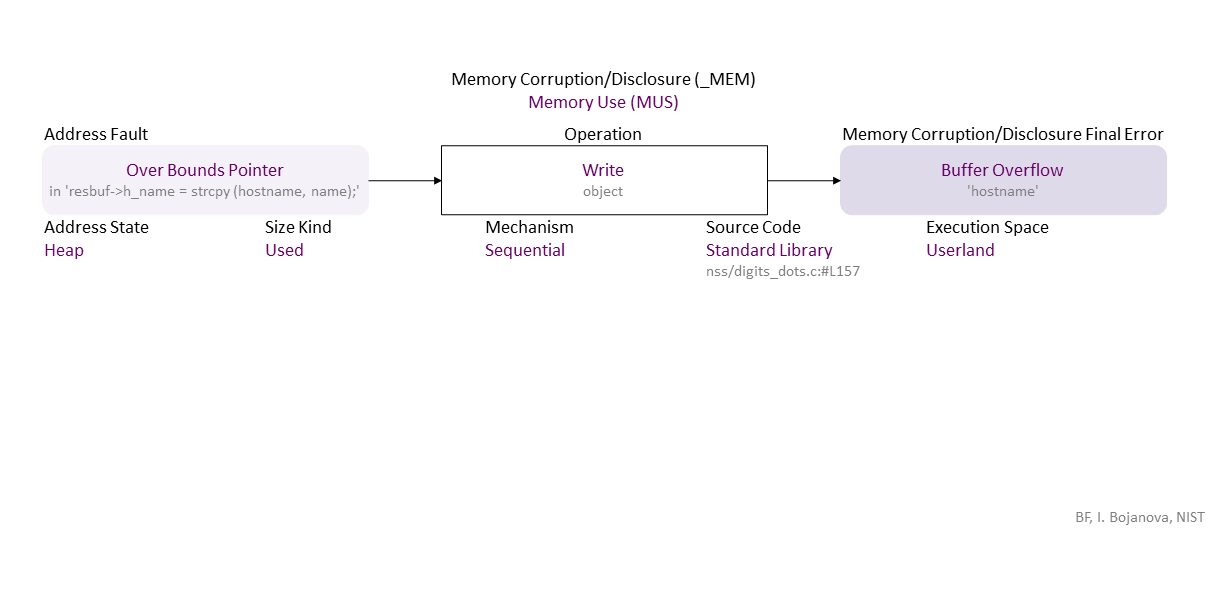
, which propagates to Overbound Pointer (in ‘resbuf->h_name = strcpy (hostname, name);’) Sequential Write (object) Heap Used Standard Library (nss/digits_dots.c:#L157) in Userland that results in Buffer Overflow (‘hostname’)
, which can be exploited toward ACE (everything could be lost) security failure.
|
| Class | Definition |
| TCM | Type Computation (TCM) class – An arithmetic expression (over numbers, strings, or pointers) is calculated improperly, or a boolean condition is evaluated improperly. |
| MMN | Memory Management (MMN) class – An object is allocated, resized, or deallocated improperly. |
| MAD | Memory Addressing (MAD) class – The pointer to an object is initialized, dereferenced, repositioned, or reassigned to an improper memory address. |
| MUS | Memory Use (MUS) class – An object is initialized, read, written, or cleared improperly. |
| Operation | Definition |
| Calculate | Calculate operation – Find the result of a numeric, pointer, or string operation. |
| Reallocate-Reduce | Reallocate-Reduce operation – Reserve a new smaller space in memory for an object at a new address, reassign the pointer, and release the previous piece of memory. |
| Reposition | Reposition operation – Change the pointer to another position inside its object. |
| Write | Write operation – Change the data value of an object in memory to another meaningful value. |
| Cause/Consequence | Definition |
| Code Bug | Code Bug type – An error in the implementation of an operation – proper operands over an improper operation. It is the roor cause of a security vulnerability. Must be fixed to resolve the vulnerability. |
| Erroneous Code | Erroneous Code bug - There is a coding error in the implementation of the operation. |
| Data Error/Fault | Data Fault/Error type – The data of an object has harmed semantics or inconsistent or wrong value. |
| Wrong Result | Wrong Result fault/error – Incorrect value – from type conversion or computation. |
| Wrong Size | Wrong Size fault/error – The value used as size or length (i.e., the number of elements) does not match the object's memory size or length (e.g., to limit a pointer reposition or index increment/decrement in a repetition statement). |
| Size Error/Fault | Type Fault/Error type – The set or range of allowed values of an entity is wrong or the operations allowed on them are wrong. |
| Insufficient Size | Insufficient Size fault/error – The allocated memory is too little for the data it should store. |
| Address Error/Fault | Address Fault/Error type – The address of an object is wrong. |
| Overbound Pointer | Overbound Pointer fault/error – Holds an address that is above the upper boundary of its object. |
| Memory Corruption/Disclosure Final Error | Memory Corruption/Disclosure final error type – An exploitable or undefined system behavior caused by memory addressing, allocation, use, or deallocation bugs. |
| Buffer Overflow | Buffer Overflow final error – Write data above the upper bound of an object (i.e., buffer overwrite). |
| Operation Attribute | Definition |
| Mechanism | Mechanism operation attribute type – Shows how the operation the operation with a bug or faulty operand is performed. |
| Operator | Operator operation attribute – The operation is via a function with a symbolic name that implements a mathematical, relational or logical operation. |
| Explicit | Explicit operation attribute – The operation is via a function/method call. |
| Sequential | Sequential operation attribute – The operation is via iterating over the object elements. |
| Source Code | Source Code operation attribute type – Shows where the code of the operation with a bug or faulty operand resides within the software, firmware, or hardware. |
| Standard Library | Standard Library operation attribute – The operation code is in the standard library for a particular programming language. |
| Execution Space | Execution Space operation attribute type – Shows where the operation with a bug or faulty operand is executed and the privilege level at which it runs. |
| Local | Local operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with access control policy with limited (local user) permission. |
| Userland | Userland operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with privilege levels, but in unprivileged mode (e.g., ring 3 in x86 architecture). |
| Operand Attribute | Definition |
| Name State | Name State operand attribute type – Shows what the stage of the entity name is. |
| Bound | Bound operand attribute – The name is linked to a declared (or inferred) data type, a defined object's data, or a called function implementation. |
| Data Kind | Data Kind operand attribute type – Shows what the type or category of data is. |
| Numeric | Numeric operand attribute – A number – a sequence of digits. |
| Type Kind | Type Kind operand attribute type – Shows what the data type composition is. |
| Primitive | Primitive operand attribute – A scalar data type that mimics the hardware units - e.g., int (long, short, signed), float, double, string, Boolean. A primitive data type is only language defined and is not built from other data types. |
| Address State | Address State operand attribute type – Shows where the address is (i.e., its location) in the memory layout. |
| Heap | The object is a dynamically allocated data structure (e.g., via malloc() and new). |
| Size Kind | Size Kind operand attribute type – Shows what is used as the size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of an object - e.g., as the limit for traversal over the elements. |
| Used | Used operand attribute – A supplied value to be used as the size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of an object. |