BF Specification of CVE-2017-17833 SLPD Double Free in OpenSLP in v1.0.2 and v1.1.0
-0.png)
Missing reposition of the 'result' pointer leads to a dangling pointer due to reallocation of the same object via 'sendbuf', which, when used to resize (second reallocation) the object leads to a Double Deallocate -- aka double free. If exploited, this can lead to a denial of service (DOS) --availability loss, or arbitrary code execution (ACE) and more specificqlly remote code execution (RCE) -- everything could be lost.
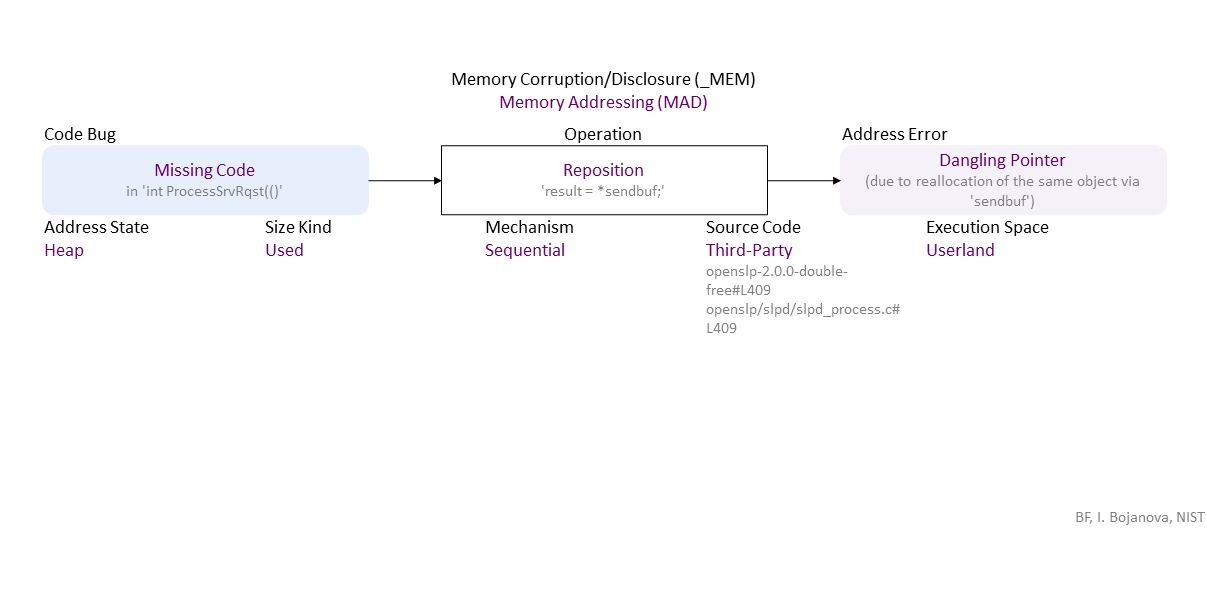
//generated// Missing Code (in ‘int ProcessSrvRqst(()’) to Sequential Reposition ‘result = *sendbuf;’ Heap Used in Third-Party (openslp-2.0.0-double-free#L409 openslp/slpd/slpd_process.c#L409) Userland leads to Dangling Pointer ((due to reallocation of the same object via ‘sendbuf’))
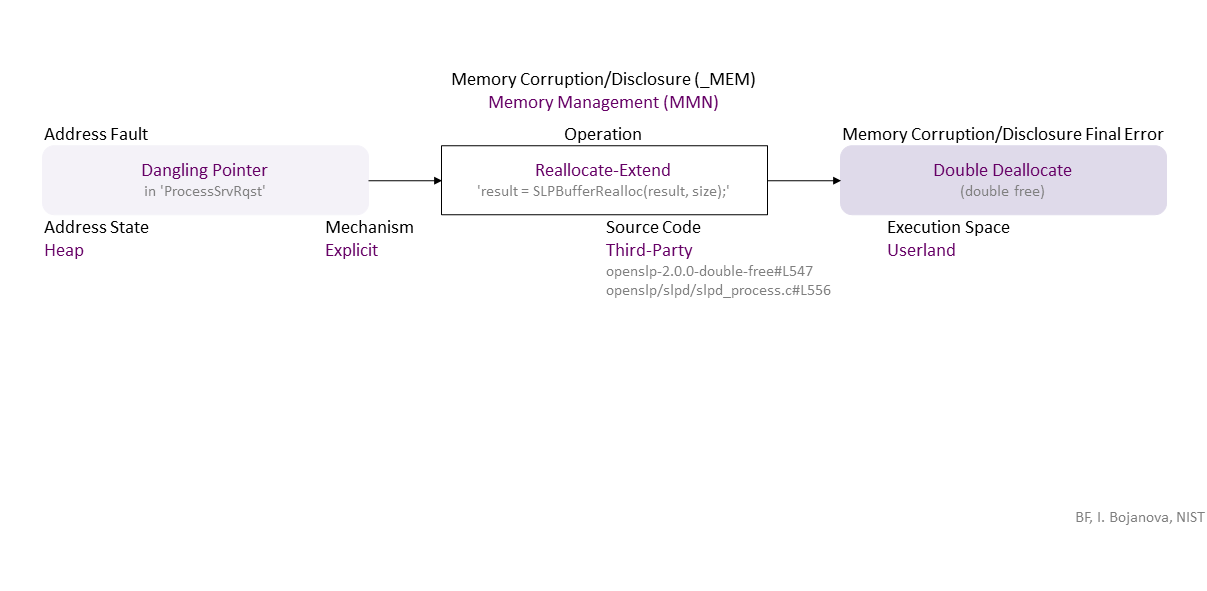
, which propagates to Dangling Pointer (in ‘ProcessSrvRqst’) Explicit Reallocate-Extend (‘result = SLPBufferRealloc(result, size);’) Heap Third-Party (openslp-2.0.0-double-free#L547 openslp/slpd/slpd_process.c#L556) in Userland that results in Double Deallocate ((double free))
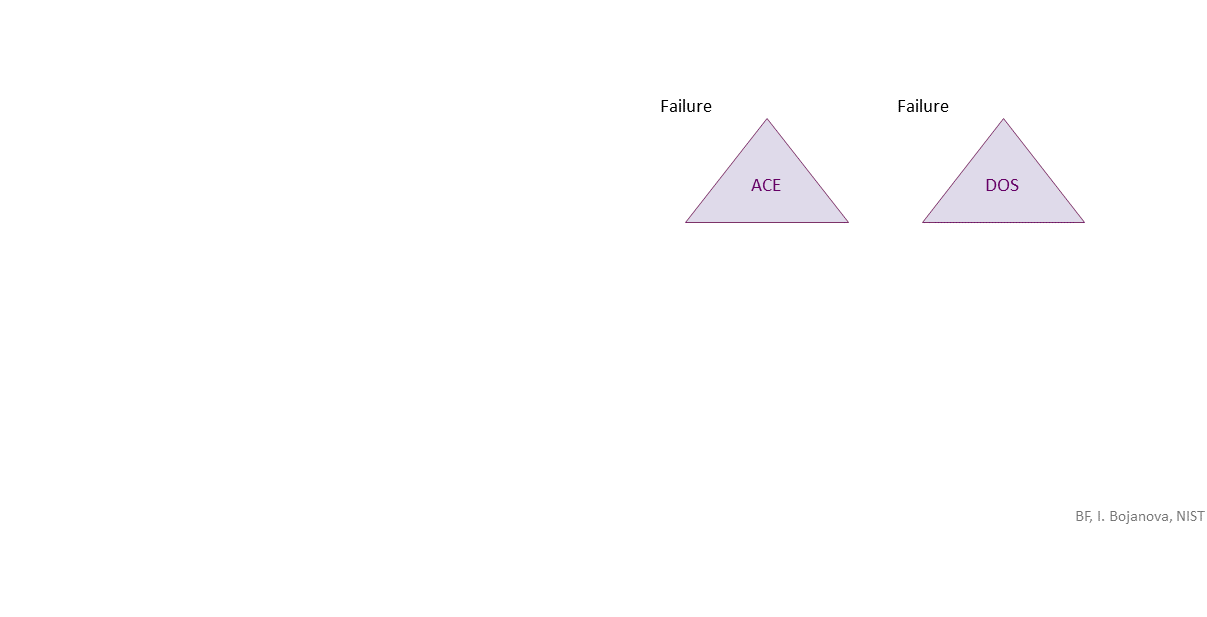
, which can be exploited toward ACE (RCE) (everything could be lost) or DOS (availability loss) security failure.
|
| Class | Definition |
| MAD | Memory Addressing (MAD) class – The pointer to an object is initialized, dereferenced, repositioned, or reassigned to an improper memory address. |
| MMN | Memory Management (MMN) class – An object is allocated, resized, or deallocated improperly. |
| Operation | Definition |
| Reposition | Reposition operation – Change the pointer to another position inside its object. |
| Reallocate-Extend | Reallocate-Extend operation – Reserve a new larger piece of memory for an object at a new address, reassign its pointer, and release the previous piece of memory. |
| Cause/Consequence | Definition |
| Code Bug | Code Bug type – An error in the implementation of an operation – proper operands over an improper operation. It is the roor cause of a security vulnerability. Must be fixed to resolve the vulnerability. |
| Missing Code | Missing Code bug - The operation is misplaced entirely absent. |
| Address Error/Fault | Address Fault/Error type – The address of an object is wrong. |
| Dangling Pointer | Dangling Pointer fault/error – Still holds the address of its successfully deallocated object (e.g., a pointer to a freed heap object or address of a stack object returned by a function). |
| Memory Corruption/Disclosure Final Error | Memory Corruption/Disclosure final error type – An exploitable or undefined system behavior caused by memory addressing, allocation, use, or deallocation bugs. |
| Double Deallocate | Double Deallocate final error – An attempt to deallocate a deallocated (freed) object. |
| Operation Attribute | Definition |
| Mechanism | Mechanism operation attribute type – Shows how the operation the operation with a bug or faulty operand is performed. |
| Sequential | Sequential operation attribute – The operation is via iterating over the object elements. |
| Explicit | Explicit operation attribute – The operation is via a function/method call. |
| Source Code | Source Code operation attribute type – Shows where the code of the operation with a bug or faulty operand resides within the software, firmware, or hardware. |
| Third-Party | Third-Party operation attribute – The operation code is in a third-party source. |
| Execution Space | Execution Space operation attribute type – Shows where the operation with a bug or faulty operand is executed and the privilege level at which it runs. |
| Userland | Userland operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with privilege levels, but in unprivileged mode (e.g., ring 3 in x86 architecture). |
| Operand Attribute | Definition |
| Address State | Address State operand attribute type – Shows where the address is (i.e., its location) in the memory layout. |
| Heap | The object is a dynamically allocated data structure (e.g., via malloc() and new). |
| Size Kind | Size Kind operand attribute type – Shows what is used as the size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of an object - e.g., as the limit for traversal over the elements. |
| Used | Used operand attribute – A supplied value to be used as the size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of an object. |