BF Specification of CVE-2018-14557 Tenda firmware until v15.03.06.44_CN(AC7), v15.03.05.19(6318)_CN(AC9), and v15.03.06.23_CN(AC10)
-0.png)
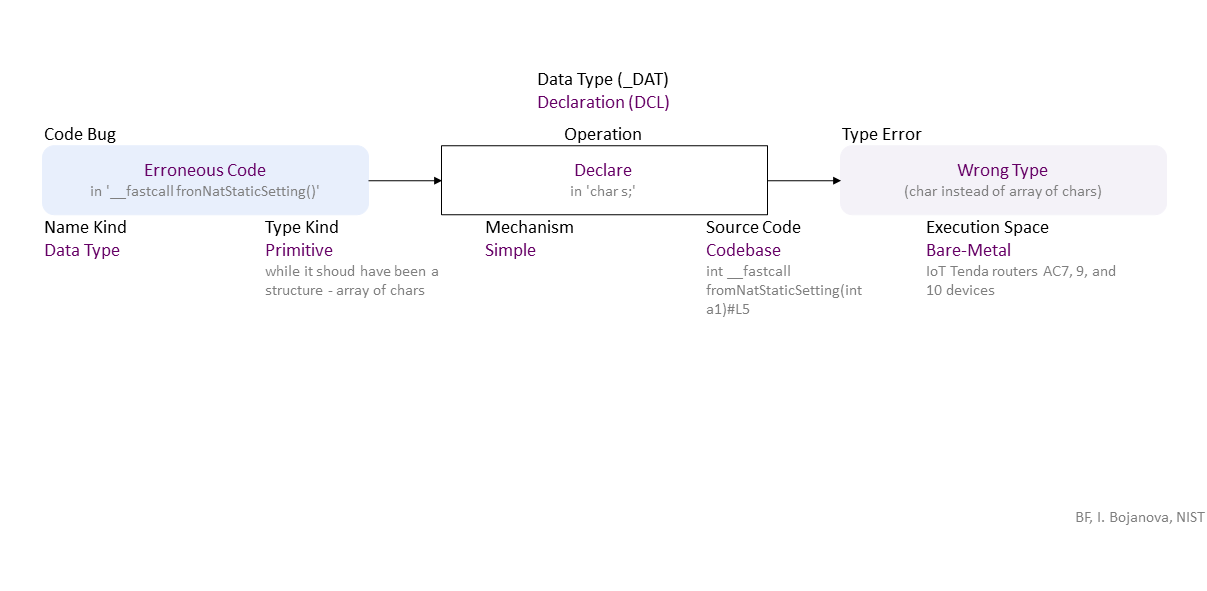
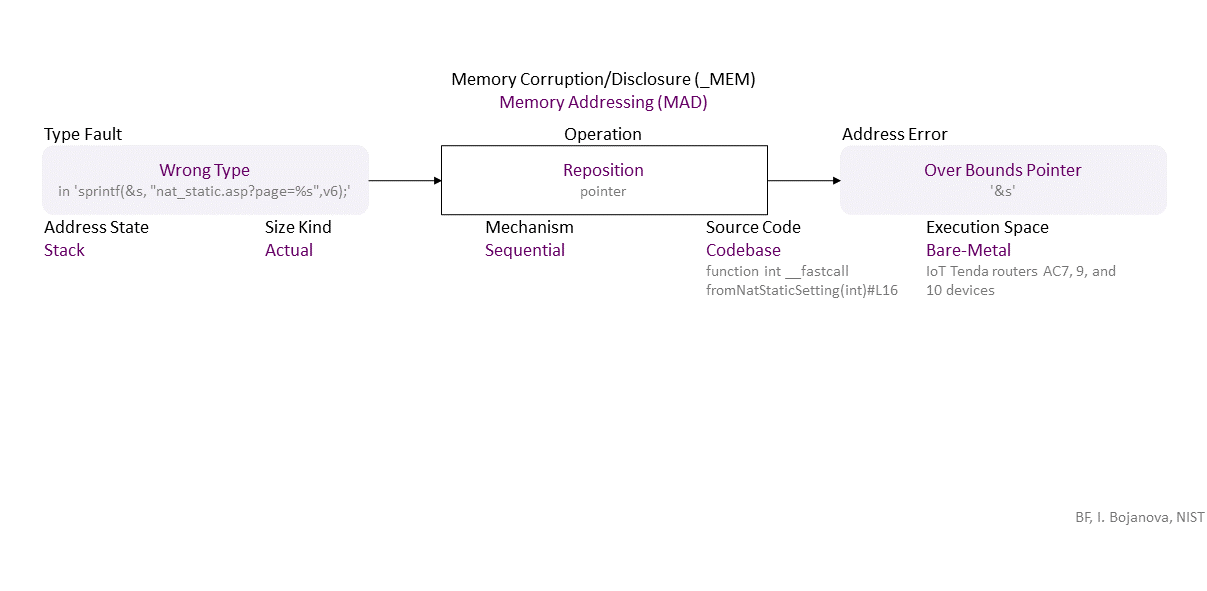
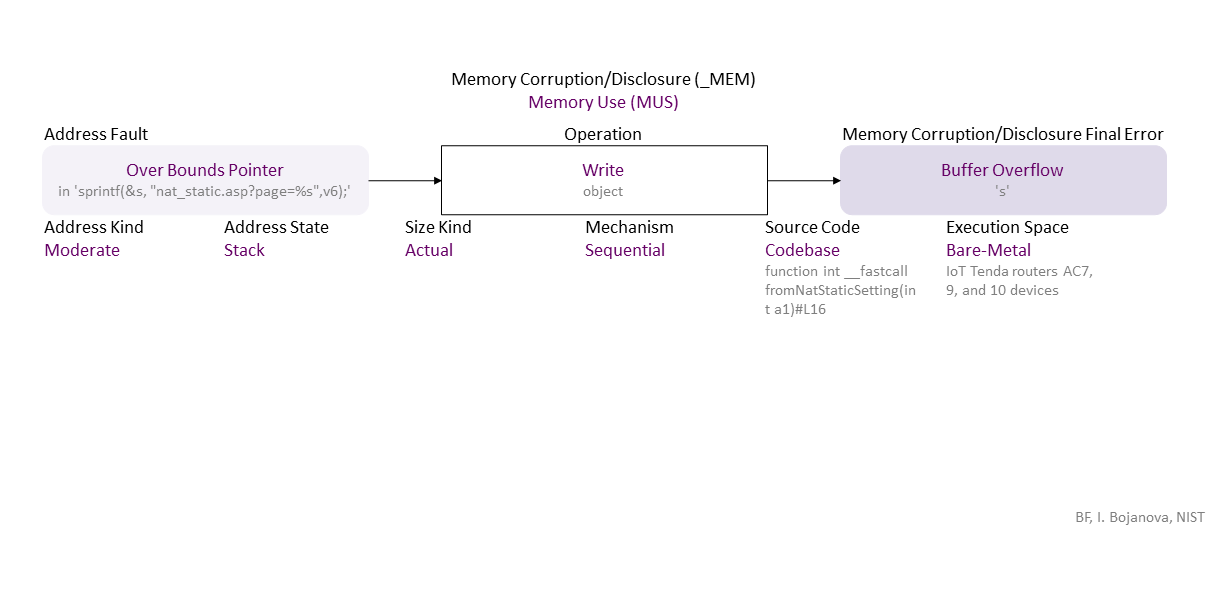
Erroneous declaration of the 's' object leads to a wrong type (char instead of an array of chars), allowing a pointer reposition over its bounds, which, when used in 'sprintf()' leads to stack buffer overflow. If exploited, this can lead to denial of service (DOS) -- availability loss.
//generated// Missing Code (in ‘int ProcessSrvRqst(()’) to Sequential Reposition ‘result = *sendbuf;’ Heap Used in Third-Party (openslp-2.0.0-double-free#L409 openslp/slpd/slpd_process.c#L409) Userland leads to Dangling Pointer ((due to reallocation of the same object via ‘sendbuf’))
, which propagates to Dangling Pointer (in ‘ProcessSrvRqst’) Explicit Reallocate-Extend (‘result = SLPBufferRealloc(result, size);’) Heap Third-Party (openslp-2.0.0-double-free#L547 openslp/slpd/slpd_process.c#L556) in Userland that results in Double Deallocate ((double free))
, which can be exploited toward ACE (RCE) (everything could be lost) or DOS (availability loss) security failure.
|
|
| Class | Definition |
| DCL | Declaration (DCL) class – An object, a function, a type, or a namespace is declared or defined improperly. |
| MAD | Memory Addressing (MAD) class – The pointer to an object is initialized, dereferenced, repositioned, or reassigned to an improper memory address. |
| MUS | Memory Use (MUS) class – An object is initialized, read, written, or cleared improperly. |
| Operation | Definition |
| Declare | Declare operation – Specify the name and type of an object; the name, return type, and parameters of a function; or the name and type parameters of a type. |
| Reposition | Reposition operation – Change the pointer to another position inside its object. |
| Write | Write operation – Change the data value of an object in memory to another meaningful value. |
| Cause/Consequence | Definition |
| Code Bug | Code Bug type – An error in the implementation of an operation – proper operands over an improper operation. A first cause for the chain of weaknesses underlying a software security vulnerability. Must be fixed to resolve the vulnerability. |
| Erroneous Code | Erroneous Code bug - There is a coding error in the implementation of the operation. |
| Type | Type Fault/Error type – The set or range of allowed values of an entity is wrong or the operations allowed on them are wrong. |
| Wrong Type | Wrong Type fault/error – A data type range or structure is not correct. |
| Address Error/Fault | Address Fault/Error type – The address of an object is wrong. |
| Overbound Pointer | Overbound Pointer fault/error – Holds an address that is above the upper boundary of its object. |
| Memory Corruption/Disclosure Final Error | Memory Corruption/Disclosure final error type – An exploitable or undefined system behavior caused by memory addressing, allocation, use, or deallocation bugs. |
| Buffer Overflow | Buffer Overflow final error – Write data above the upper bound of an object (i.e., buffer overwrite). |
| Operation Attribute | Definition |
| Mechanism | Mechanism operation attribute type – Shows how the operation the operation with a bug or faulty operand is performed. |
| Simple | Simple operation attribute – The operation is via non-polymorphic types. |
| Sequential | Sequential operation attribute – The operation is via iterating over the object elements. |
| Source Code | Source Code operation attribute type – Shows where the code of the operation with a bug or faulty operand resides within the software, firmware, or hardware. |
| Codebase | Codebase operation attribute – The operation is in the programmer's code - in the application itself. |
| Execution Space | Execution Space operation attribute type – Shows where the operation with a bug or faulty operand is executed and the privilege level at which it runs. |
| Bare-Metal | Bare-Metal operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment without privilege control. Usually, the program is the only software running and has total access to the hardware. |
| Operand Attribute | Definition |
| Name Kind | Name Kind operand attribute type – Shows what the entity with this name is. |
| Data Type | Data Type operand attribute – A set of allowed values and the operations allowed over them. |
| Type Kind | Type Kind operand attribute type – Shows what the data type composition is. |
| Primitive | Primitive operand attribute – A scalar data type that mimics the hardware units - e.g., int (long, short, signed), float, double, string, Boolean. A primitive data type is only language defined and is not built from other data types. |
| Address State | Address State operand attribute type – Shows where the address is (i.e., its location) in the memory layout. |
| Stack | |
| Size Kind | Size Kind operand attribute type – Shows what is used as the size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of an object - e.g., as the limit for traversal over the elements. |
| Actual | Actual operand attribute – The real size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of the allocated memory for an object. |
| Address Kind | Address Kind operand attribute type - Shows how much memory is accessed (i.e., the span) outside the bounds of an object. |
| Moderate |