BF Specification of CVE-2021-21834 Bad Alloc in GPAC v1.0.1
-0.png)
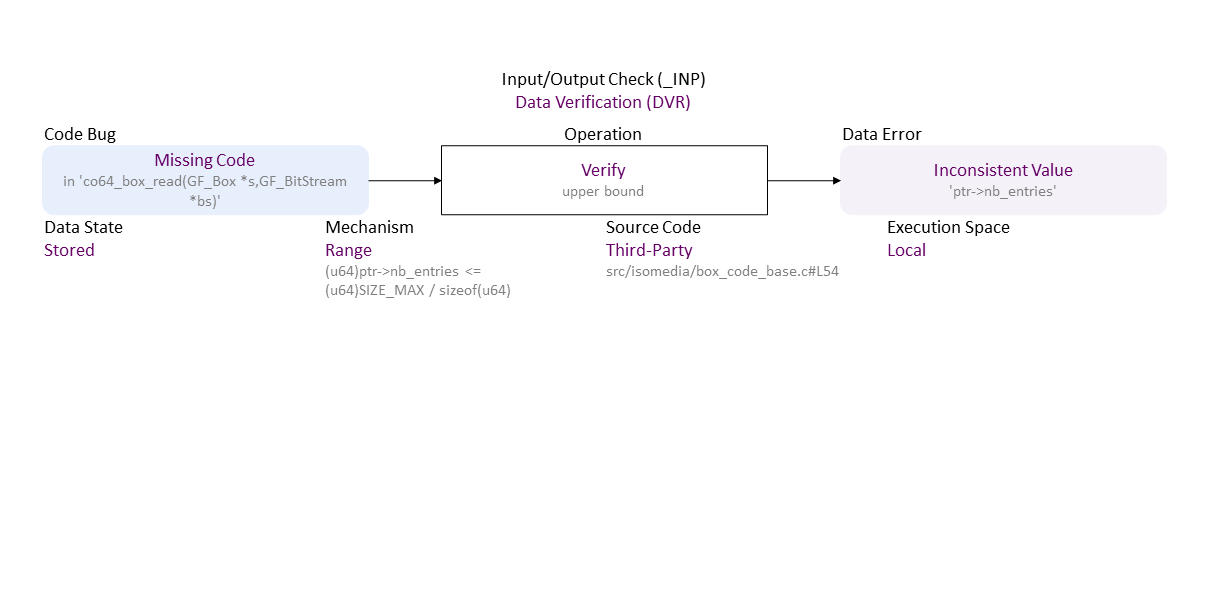
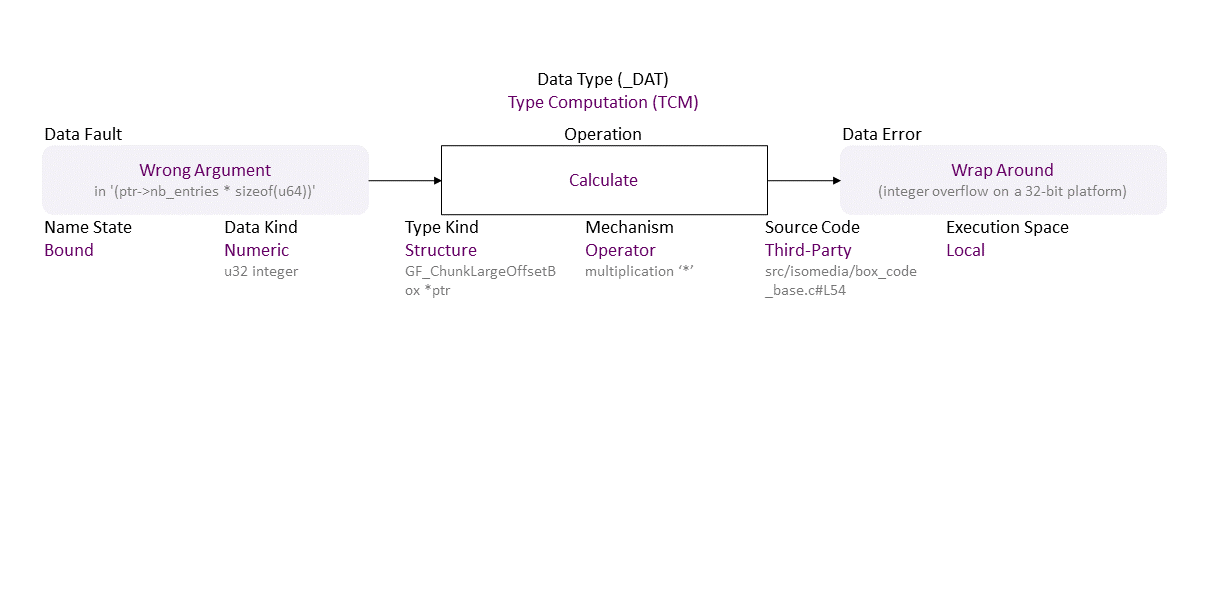
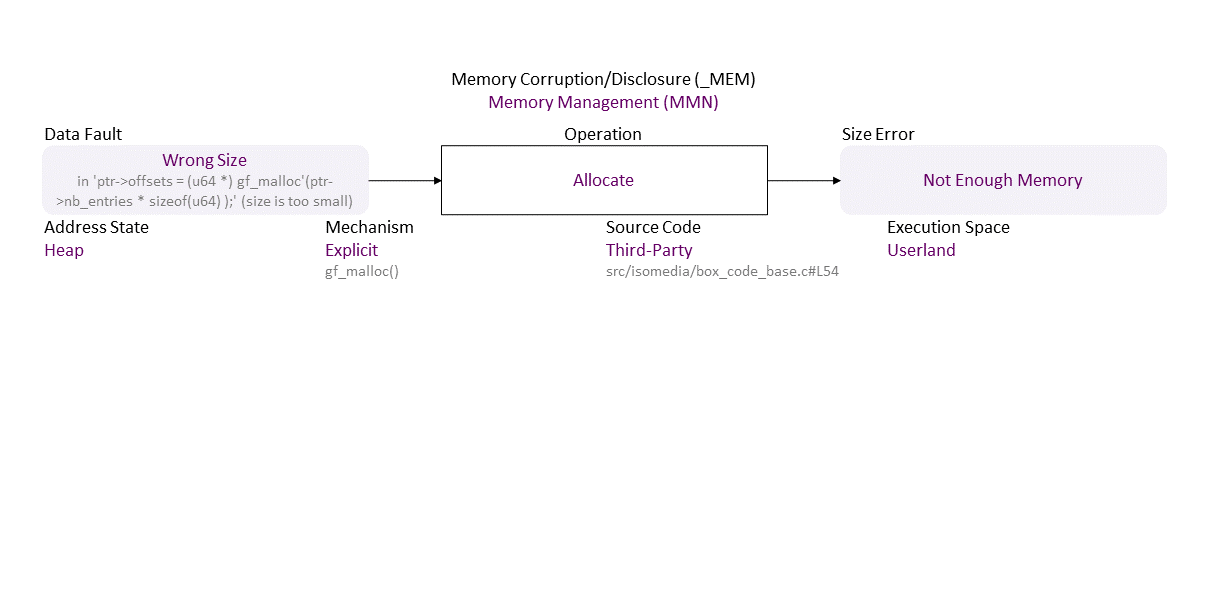
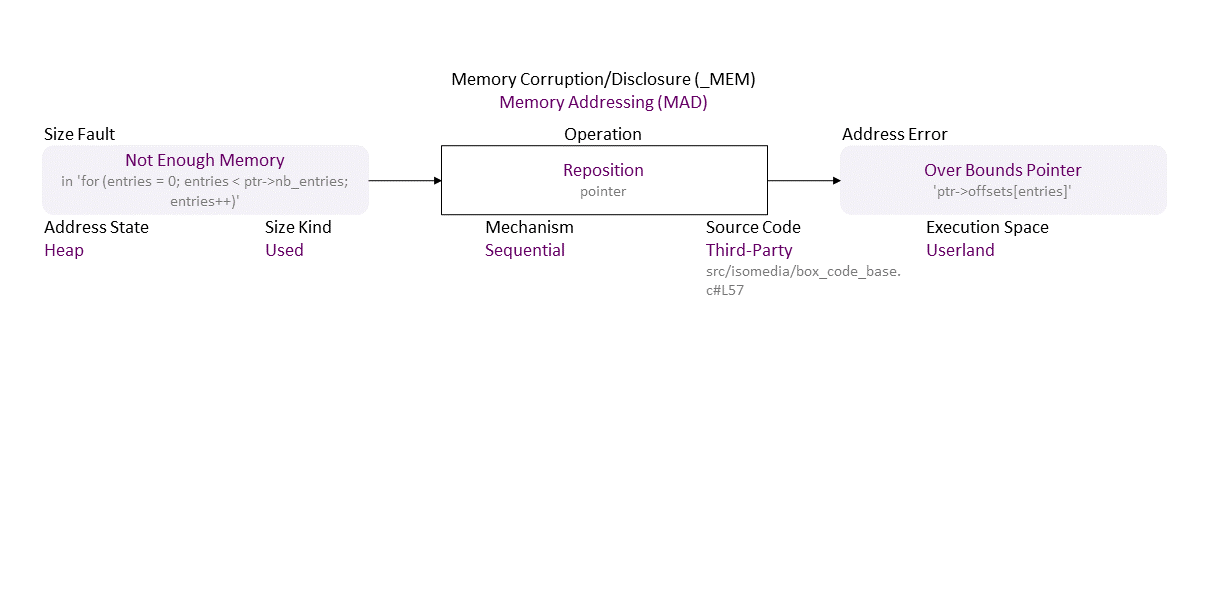
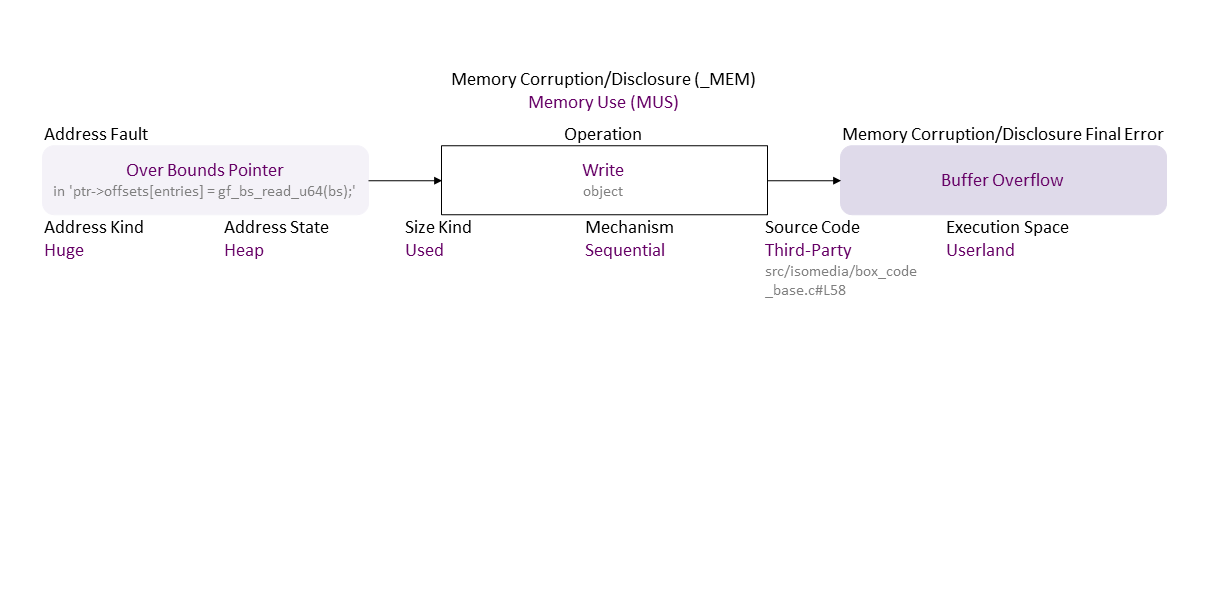
Missing verification on the range for the user-controlled 'nb_entries' ((u64)ptr->nb_entries * sizeof(u64) must not be greater than a 32-bit int) results in an inconsistent value, which becomes a wrong argument for the multiplication ‘*’ operator in 'ptr->nb_entries * sizeof(u64)' . The result wraps around (integer overflow on a 32-bit platform) and becomes a small number used to allocate not enough memory for the 'ptr->offsets[entries]' buffer, allowing a pointer reposition over its bounds, which, when used to write leads to a heap buffer overflow. If exploited, this can lead to denial of service or arbitrary (remote) code execution.
vendor:product: gpac:gpac:1.0.1 |
| Class | Definition |
| DVR | Data Verification (DVR) class – Data are verified (semantics check) or corrected (assign, remove) improperly. |
| TCM | Type Computation (TCM) class – An arithmetic expression (over numbers, strings, or pointers) is calculated improperly, or a boolean condition is evaluated improperly. |
| MMN | Memory Management (MMN) class – An object is allocated, deallocated, or resized improperly. |
| MAD | Memory Addressing (MAD) class – The pointer to an object is initialized, repositioned, or reassigned to an improper memory address. |
| MUS | Memory Use (MUS) class – An object is initialized, read, written, or cleared improperly. |
| Operation | Definition |
| Verify | Verify operation – Check data semantics (proper value/meaning) in order to accept (and possibly correct) or reject it. |
| Calculate | Calculate operation – Find the result of a numeric, pointer, or string operation. |
| Allocate | Allocate operation – Reserve space in memory for an object; defines its initial boundaries and size. |
| Reposition | Reposition operation – Change the pointer to another position inside its object. |
| Write | Write operation – Change the data value of an object to another meaningful value. |
| Cause/Consequence | Definition |
| Code Bug | Code Bug type – Defect in the implementation of the operation – proper operands over an improper operation. A first cause for the chain of weaknesses underlying a software security vulnerability. Must be fixed to resolve the vulnerability. |
| Missing Code | Missing Code bug - The operation is entirely absent. |
| Data Error/Fault | Data Fault/Error type – The object data has harmed semantics or inconsistent or wrong value. |
| Inconsistent Value | Inconsistent Value fault/error – Data value does not correspond to the value of a related data (e.g., inconstancy between the value of a size variable and the actual buffer size). |
| Wrong Argument | Wrong Argument fault/error – Inaccurate input data value, i.e., non-verified for harmed semantics. |
| Wrap Around | Wrap Around fault/error – A moved around-the-clock value over its data type upper or lower range, as it exceeds that range. (Integer Over-/Under-flow is a wrapped-around the upper/lower range integer value; may become very small/large and change to the opposite sign. |
| Wrong Size | Wrong Size fault/error – The value used as size does not match the actual size of the object (e.g., to restrict pointer repositioning or index increment/decrement in a repetition statement). |
| Size Error/Fault | Size Fault/Error type – The object size in use is wrong. |
| Not Enough Memory | Not Enough Memory fault/error – The allocated memory is too little for the data it should store. |
| Address Error/Fault | Address Fault/Error type – The object address in use is wrong. |
| Over Bounds Pointer | Over Bounds Pointer fault/error – Holds an address above the upper boundary of its object. |
| Memory Corruption/Disclosure Final Error | Memory Corruption/Disclosure exploitable error type – An exploitable or undefined system behavior caused by memory addressing, allocation, use, and deallocation bugs. |
| Buffer Overflow | Buffer Overflow exploitable error – Writing above the upper bound of an object – aka Buffer Over-Write. |
| Operation Attribute | Definition |
| Mechanism | Mechanism operation attribute type – Shows how the buggy/faulty operation code is performed. |
| Range | Range operation attribute – The operation checks data are within a (min, max) interval. |
| Operator | Operator operation attribute – The operation is via a function with a symbolic name that implements a mathematical, relational or logical operation. |
| Explicit | Explicit operation attribute – The operation is via a function/method call. |
| Sequential | Sequential operation attribute – The operation is via iterating over the object elements. |
| Source Code | Source Code operation attribute type – Shows where the operation with the bug or a faulty operand is in the program – in what kind of software. |
| Third-Party | Third-Party operation attribute – The operation code is in a third-party software. |
| Execution Space | Execution Space operation attribute type – Shows where the buggy/faulty operation code is running or with what privilege level. |
| Local | Local operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with access control policy with limited (local user) permission. |
| Userland | Userland operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with privilege levels, but in unprivileged mode (e.g., ring 3 in x86 architecture). |
| Operand Attribute | Definition |
| Data State | Data State operand attribute type operand attribute – Shows where the data come from. |
| Stored | Stored operand attribute – Data are from a permanent storage (e.g., file, database on a storage device); they are at rest. |
| Name State | Name State operand attribute type – Shows at what stage the entity name is. |
| Bound | Bound operand attribute – The name is linked to a declared (or inferred) data type, a defined object's data, or a called function implementation. |
| Data Kind | Data Kind operand attribute type – Shows what the data value is. |
| Numeric | Numeric operand attribute – A number – a sequence of digits. |
| Type Kind | Type Kind operand attribute type – Shows what the data type composition is. |
| Structure | Structure operand attribute – A composite data type - e.g., array, list, map, class. A structured data type is built from other data types and has primitive or structured members. |
| Address State | Address State operand attribute type - State operand attribute type – Shows where the address is in the memory layout. |
| Heap | Heap operand attribute – The object is a dynamically allocated data structure (e.g., via malloc() and new). |
| Size Kind | Size Kind operand attribute type – Shows what the limit for traversal of the object is. |
| Used | Used operand attribute – A supplied size for an object. |
| Address Kind | Address Kind operand attribute type - Shows what the accessed outside object's bounds memory is. |
| Huge | Huge operand attribute - More than 1 KB of memory. |