BF Specification of CVE-2004-1287 — Stack Buffer Overflow in NASM 0.98.38 1.2
-0.png)
Missing verification of 'arg' towards a upper limit leads to use of an inconsistent size for an object, allowing a pointer reposition over its bounds, which, when used in ‘vsprintf()' leads to a stack buffer overflow. If exploited, this can lead to data tampering, denial of service (application crash), or remote code execution.
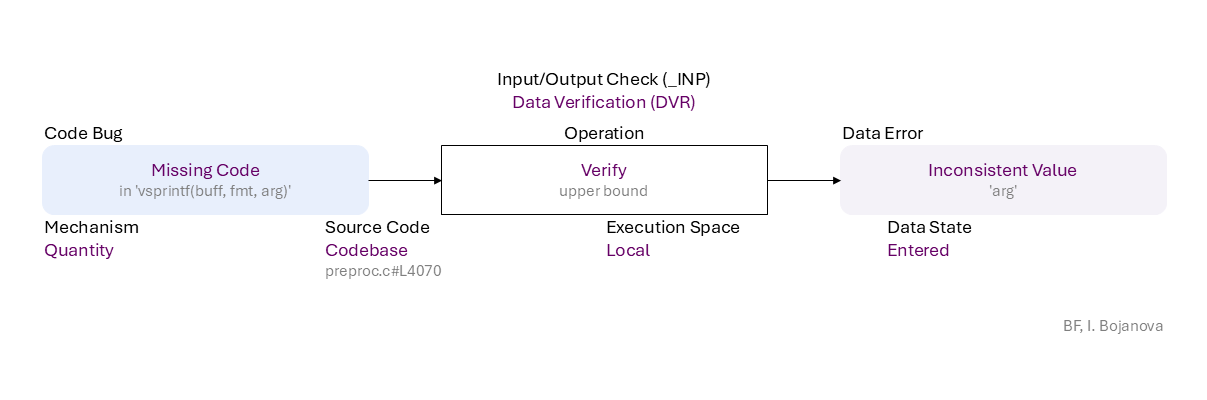
Missing Code (in 'vsprintf(buff, fmt, arg)') to Verify (upper bound) of Entered data using Quantity mechanism in Codebase source code (preproc.c#L4070) in Local execution space leads to Inconsistent Value ('arg') error, which propagates to
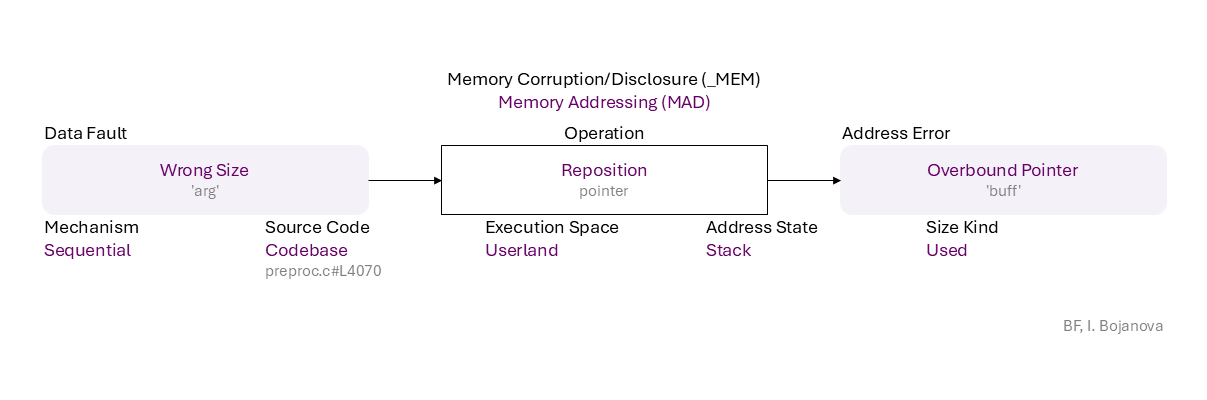
Wrong Size ('arg') to Reposition (pointer) on Stack with Used size using Sequential mechanism in Codebase source code (preproc.c#L4070) in Userland execution space that results in Overbound Pointer ('buff') error, which propagates to
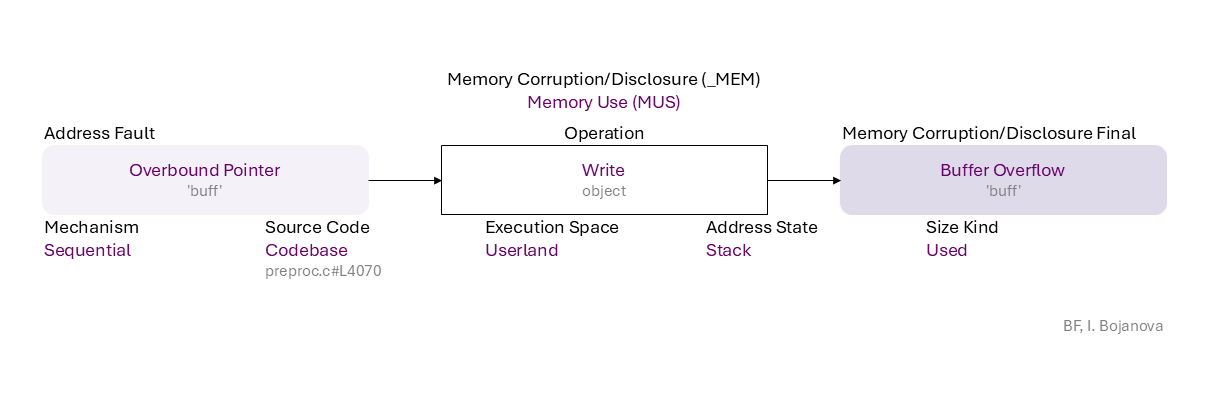
Overbound Pointer ('buff') to Write (object) on Stack with Used size using Sequential mechanism in Codebase source code (preproc.c#L4070) in Userland execution space that results in Buffer Overflow ('buff') final error, which can be exploited toward
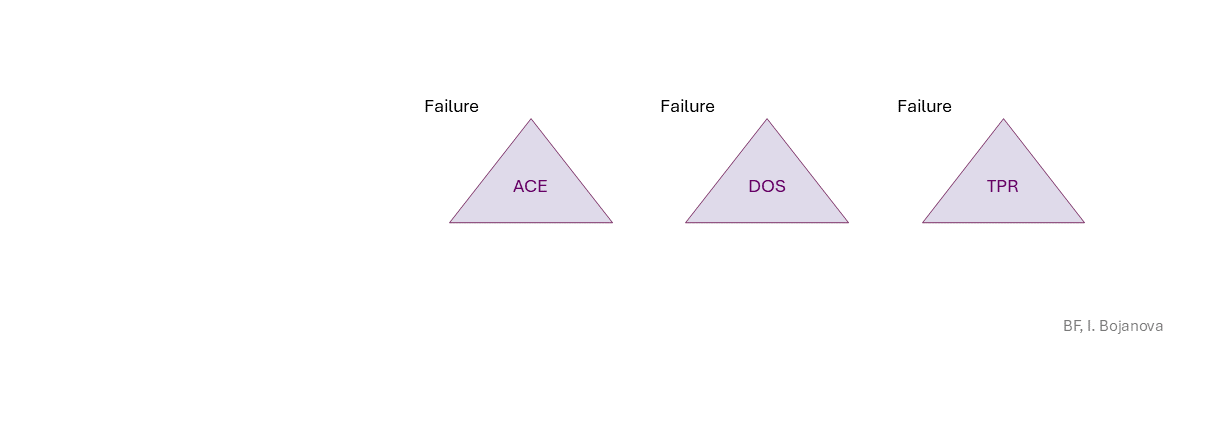
Arbitrary Code Execution (ACE) (- Remote Code Execution (RCE) - everything could be lost),Denial of Service (DOS) (availability loss),Data Tampering (TPR) (integrity loss) security failure.
|
|
| Class | Definition |
| DVR | Data Verification (DVR) class – Data are verified (i.e., semantics check) or corrected (i.e., assign or remove) improperly. |
| MAD | Memory Addressing (MAD) class – The pointer to an object is initialized, dereferenced, repositioned, or reassigned to an improper memory address. |
| MUS | Memory Use (MUS) class – An object is initialized, read, written, or cleared improperly. |
| Operation | Definition |
| Verify | Verify operation – Check data semantics (e.g., proper value/meaning) in order to accept (and possibly correct) or reject it. |
| Reposition | Reposition operation – Change the pointer to another position inside its object. |
| Write | Write operation – Change the data value of an object in memory to another meaningful value. |
| Cause/Consequence | Definition |
| Code Bug | Code Bug type – An error in the implementation of an operation – proper operands over an improper operation. It is the roor cause of a security vulnerability. Must be fixed to resolve the vulnerability. |
| Missing Code | Missing Code bug - The operation is misplaced entirely absent. |
| Data Error/Fault | Data error (or fault) type – The data of an object has harmed semantics or inconsistent or wrong value. |
| Inconsistent Value | Inconsistent Value error (or fault) – The data value does not correspond to related data value (e.g., inconstancy between the value of a size variable and the actual buffer size). |
| Wrong Size | Wrong Size error (or fault) – The value used as size or length (i.e., the number of elements) does not match the object's memory size or length (e.g., to limit a pointer reposition or index increment/decrement in a repetition statement). |
| Address Error/Fault | Address error (or fault) type – The address of an object is wrong. |
| Overbound Pointer | Overbound Pointer error (or fault) – Holds an address that is above the upper boundary of its object. |
| Memory Corruption/Disclosure Final Error | Memory Corruption/Disclosure final error/exploit vector type – An exploitable or undefined system behavior caused by memory addressing, allocation, use, or deallocation bugs. |
| Buffer Overflow | Buffer Overflow final error – Write data above the upper bound of an object (i.e., buffer over-write). |
| Operation Attribute | Definition |
| Mechanism | Mechanism operation attribute type – Shows how the operation with a bug or faulty operand is performed. |
| Quantity | Quantity operation attribute – The operation checks data for a specific measurable value (e.g., size, time, rate, frequency). |
| Sequential | Sequential operation attribute – The operation is via iterating over the object elements. |
| Source Code | Source Code operation attribute type – Shows where the code of the operation with a bug or faulty operand resides within the software, firmware, or hardware. |
| Codebase | Codebase operation attribute – The operation is in the programmer's code - in the application itself. |
| Execution Space | Execution Space operation attribute type – Shows where the operation with a bug or faulty operand is executed and the privilege level at which it runs. |
| Local | Local operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with access control policy with limited (local user) permission. |
| Userland | Userland operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment with privilege levels, but in unprivileged mode (e.g., ring 3 in x86 architecture). |
| Operand Attribute | Definition |
| Data State | Data State operand attribute type – Shows where the data comes from. |
| Entered | Entered operand attribute – Data are from a user via a user interface (e.g., input field, dialog or a command prompt). |
| Address State | Address State operand attribute type – Shows where the address is (i.e., its location) in the memory layout. |
| Stack | The object is a non-static local variable (defined in a function, a passed parameter, or a function return address). |
| Size Kind | Size Kind operand attribute type – Shows what is used as the size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of an object - e.g., as the limit for traversal over the elements. |
| Used | Used operand attribute – A supplied value to be used as the size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of an object. |
| Failure | Definition |
| ACE | Arbitrary Code Execution (ACE) – Execution of unauthorized commands or code execution that could lead to everything being lost; remote code execution (RCE) is a sub-case of ACE on a target system or device from a remote location, typically over a network. |
| DOS | Denial of Service (DOS) – Disruption of access to or use of information or information systems that leads to availability loss. |
| TPR | Data Tampering (TPR) – Unauthorized modification or destruction of information that leads to integrity loss. |