BF Specification of CVE-2007-6429 — Integer overflows in X.Org Xserver before 1.4.1
-0.png)
Missing verifications of input values leads to use of a wrong argument in a memory size calculations and wraparounds , allowing allocation of not enough memory, which, when used leads to a buffer overflow. If exploited, this can lead to arbitrary code execution.
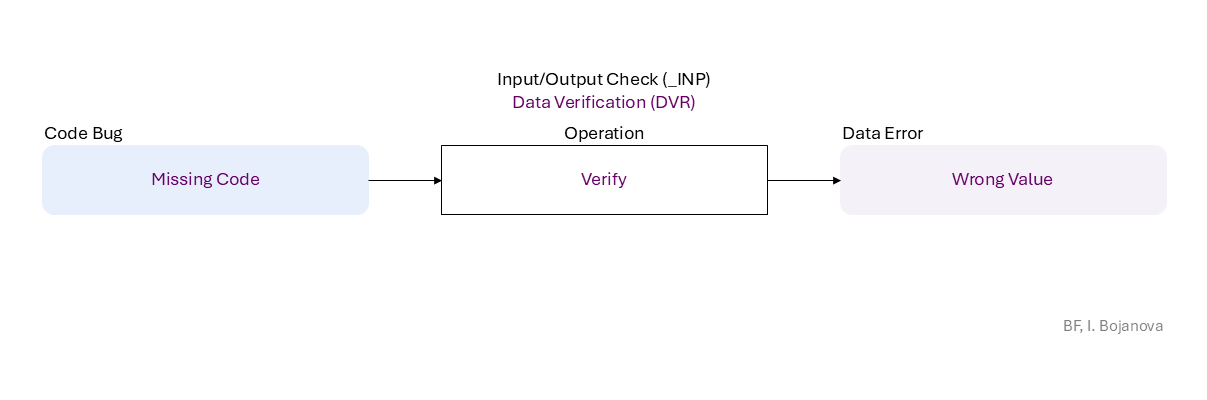
Missing Code to Verify leads to Wrong Value error, which propagates to
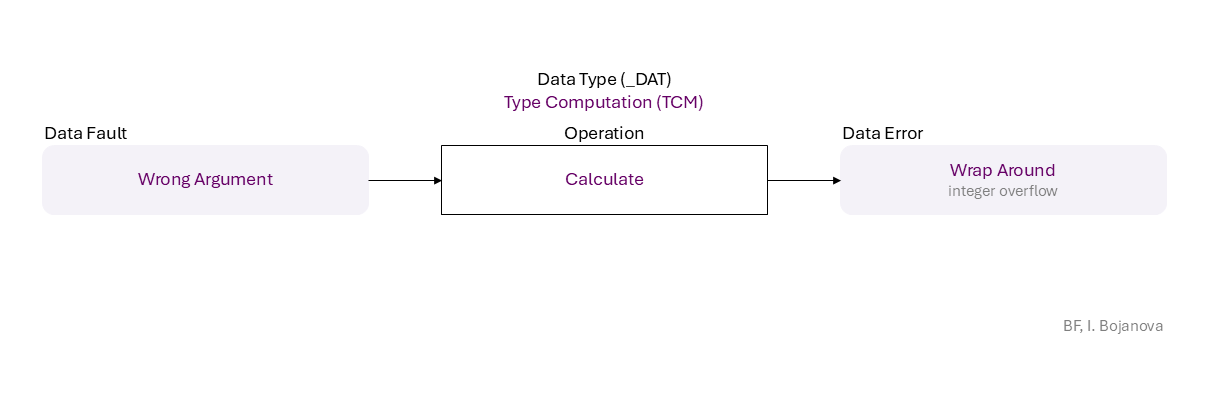
Wrong Argument to Calculate that results in Wrap Around (integer overflow) error, which propagates to
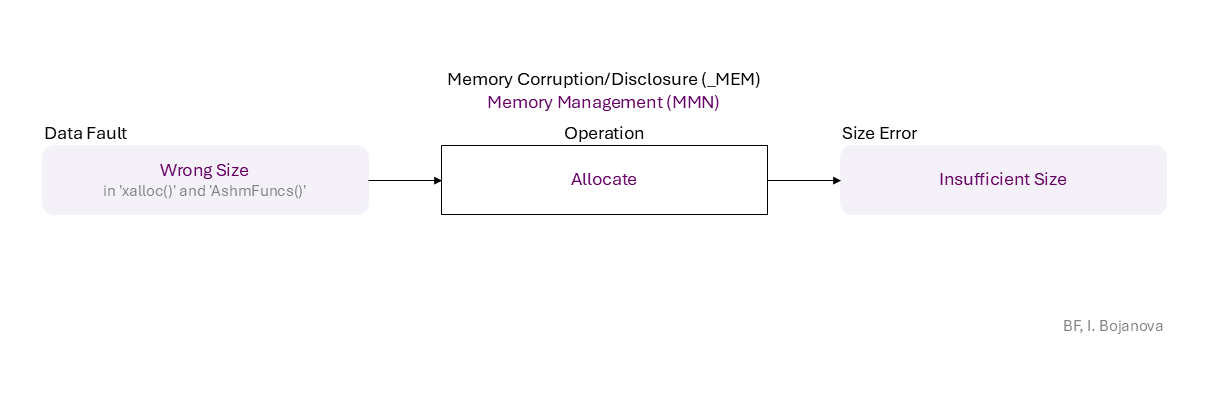
Wrong Size (in 'xalloc()' and 'AshmFuncs()') to Allocate that results in Insufficient Size error, which propagates to
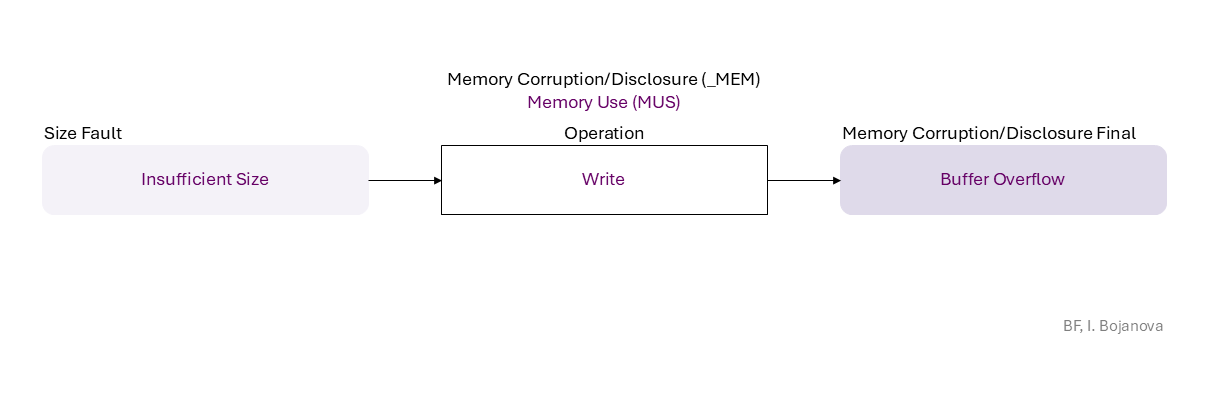
Insufficient Size to Write that results in Buffer Overflow final error, which can be exploited toward
Arbitrary Code Execution (ACE) (everything could be lost) security failure.
|
| Class | Definition |
| DVR | Data Verification (DVR) class – Data are verified (i.e., semantics check) or corrected (i.e., assign or remove) improperly. |
| TCM | Type Computation (TCM) class – An arithmetic expression (over numbers, strings, or pointers) is calculated improperly, or a boolean condition is evaluated improperly. |
| MMN | Memory Management (MMN) class – An object is allocated, resized, or deallocated improperly. |
| MUS | Memory Use (MUS) class – An object is initialized, read, written, or cleared improperly. |
| Operation | Definition |
| Verify | Verify operation – Check data semantics (e.g., proper value/meaning) in order to accept (and possibly correct) or reject it. |
| Calculate | Calculate operation – Find the result of a numeric, pointer, or string operation. |
| Allocate | Allocate operation – Reserve space in memory for an object; defines its initial boundaries and size. |
| Write | Write operation – Change the data value of an object in memory to another meaningful value. |
| Cause/Consequence | Definition |
| Code Bug | Code Bug type – An error in the implementation of an operation – proper operands over an improper operation. It is the roor cause of a security vulnerability. Must be fixed to resolve the vulnerability. |
| Missing Code | Missing Code bug - The operation is misplaced entirely absent. |
| Data Error/Fault | Data error (or fault) type – The data of an object has harmed semantics or inconsistent or wrong value. |
| Wrong Value | Wrong Value error (or fault) – The data value is not accurate (e.g., outside of a range). |
| Wrong Argument | Wrong Argument error (or fault) – Inaccurate input data value, i.e., non-verified for harmed semantics. |
| Wrap Around | Wrap Around error (or fault) – A moved around-the-clock value over its data type upper or lower range, as it exceeds that range. (Integer Over-/Under-flow is a wrapped-around the upper/lower range integer value; may become very small/large and change to the opposite sign.) |
| Wrong Size | Wrong Size error (or fault) – The value used as size or length (i.e., the number of elements) does not match the object's memory size or length (e.g., to limit a pointer reposition or index increment/decrement in a repetition statement). |
| Size Error/Fault | Type error (or fault) type – The set or range of allowed values of an entity is wrong or the operations allowed on them are wrong. |
| Insufficient Size | Insufficient Size error (or fault) – The allocated memory is too little for the data it should store. |
| Memory Corruption/Disclosure Final Error | Memory Corruption/Disclosure final error/exploit vector type – An exploitable or undefined system behavior caused by memory addressing, allocation, use, or deallocation bugs. |
| Buffer Overflow | Buffer Overflow final error – Write data above the upper bound of an object (i.e., buffer over-write). |
| Operation Attribute | Definition |
| Operand Attribute | Definition |
| Failure | Definition |
| ACE | Arbitrary Code Execution (ACE) – Execution of unauthorized commands or code execution that could lead to everything being lost; remote code execution (RCE) is a sub-case of ACE on a target system or device from a remote location, typically over a network. |