BF Specification of CVE-2022-34835 — Stack Buffer Overflow in Das U-Boot through 2022.07-rc5
-0.png)
Erroneous declaration of ‘nbytes’ as int leads to a wrong argument type for the uint ‘length’ in ‘nbytes = length’, leading to a flipped sign, and under range negative ‘linebytes’, flipped and truncated to a large integer, allowing pointer reposition over bounds, which, when used in i2c_transfer() leads to stack buffer overflow. If exploited, this can lead to denial of service – program crash, and possibly arbitrary code execution.
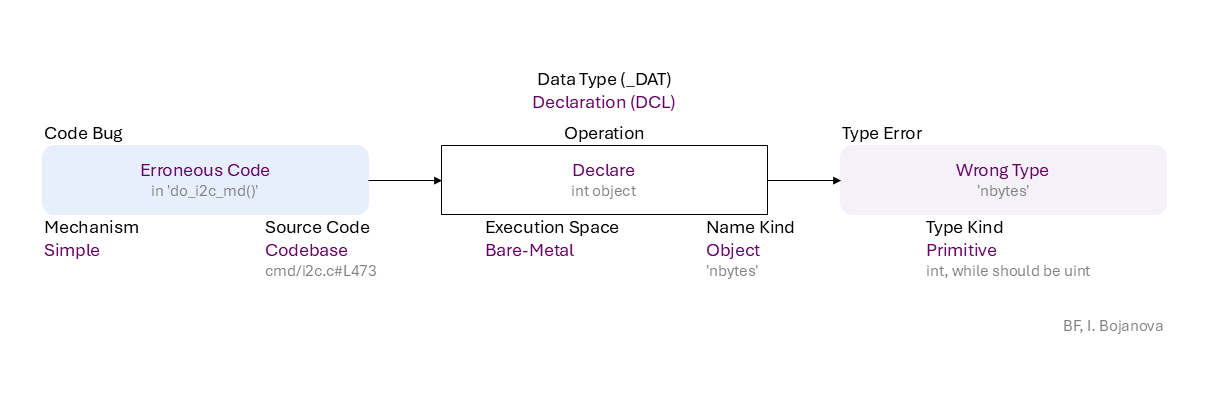
Erroneous Code (in 'do_i2c_md()') to Declare (int object) of Object name ('nbytes') of Primitive type (int, while should be uint) using Simple mechanism in Codebase source code (cmd/i2c.c#L473) in Bare-Metal execution space leads to Wrong Type ('nbytes') error, which propagates to
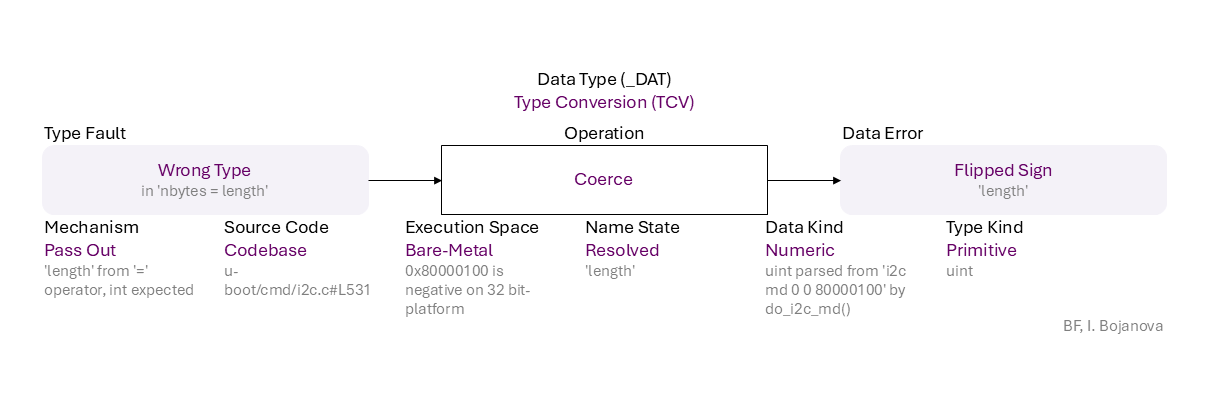
Wrong Type (in 'nbytes = length') to Coerce of Resolved name ('length') of Numeric data (uint parsed from 'i2c md 0 0 80000100' by do_i2c_md()) of Primitive type (uint) using Pass Out mechanism ('length' from '=' operator, int expected) in Codebase source code (u-boot/cmd/i2c.c#L531) in Bare-Metal execution space (0x80000100 is negative on 32 bit-platform) that results in Flipped Sign ('length') error, which propagates to
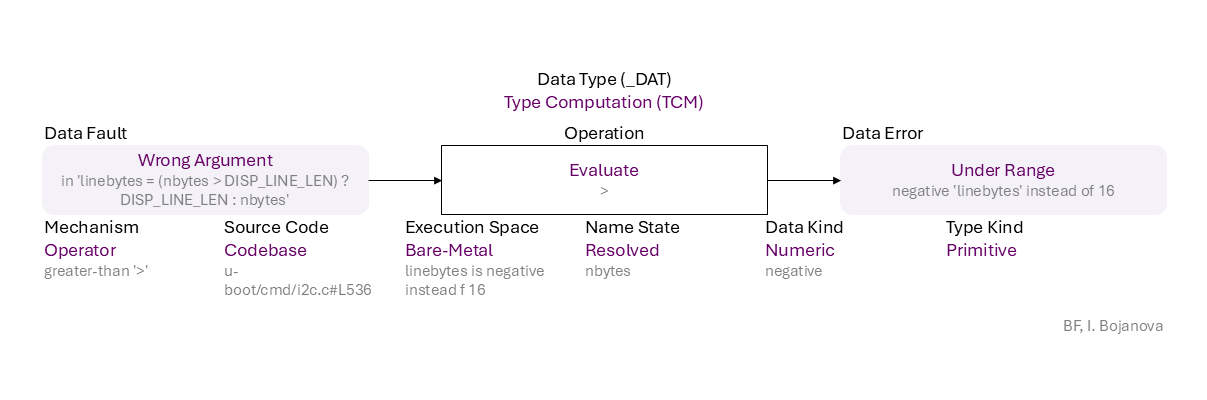
Wrong Argument (in 'linebytes = (nbytes > DISP_LINE_LEN) ? DISP_LINE_LEN : nbytes') to Evaluate (>) of Resolved name (nbytes) of Numeric data (negative) of Primitive type using Operator mechanism (greater-than '>') in Codebase source code (u-boot/cmd/i2c.c#L536) in Bare-Metal execution space (linebytes is negative instead f 16) that results in Under Range (negative 'linebytes' instead of 16) error, which propagates to
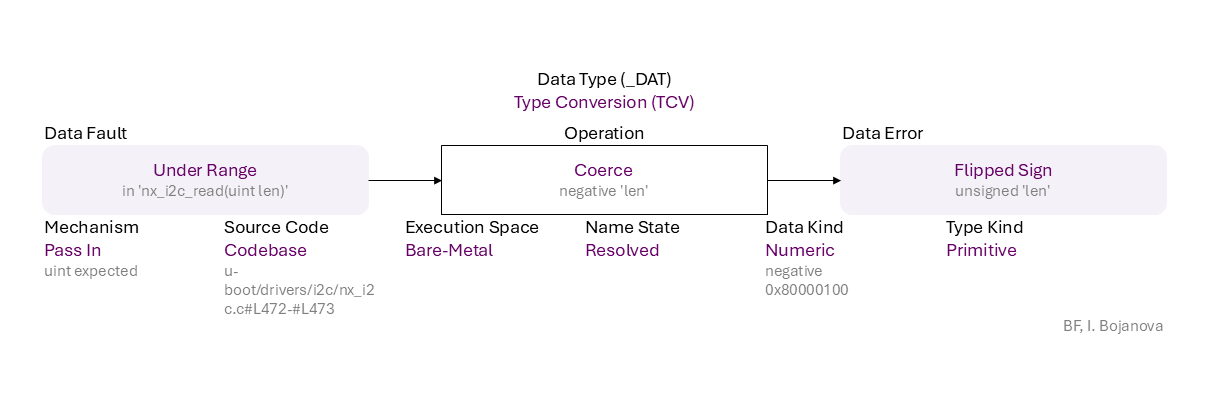
Under Range (in 'nx_i2c_read(uint len)') to Coerce (negative 'len') of Resolved name of Numeric data (negative
0x80000100) of Primitive type using Pass In mechanism (uint expected) in Codebase source code (u-boot/drivers/i2c/nx_i2c.c#L472-#L473) in Bare-Metal execution space that results in Flipped Sign (unsigned 'len') error, which propagates to
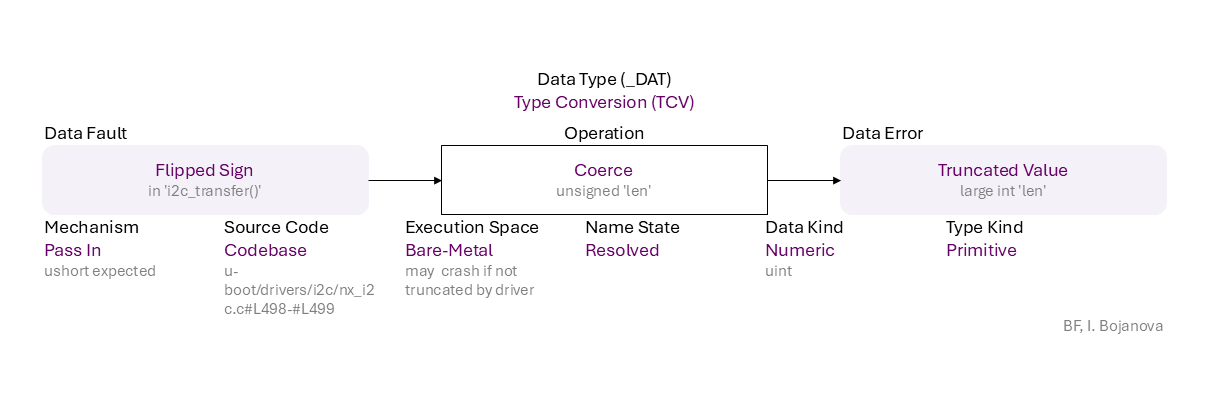
Flipped Sign (in 'i2c_transfer()') to Coerce (unsigned 'len') of Resolved name of Numeric data (uint) of Primitive type using Pass In mechanism (ushort expected) in Codebase source code (u-boot/drivers/i2c/nx_i2c.c#L498-#L499) in Bare-Metal execution space (may crash if not truncated by driver) that results in Truncated Value (large int 'len') error, which propagates to
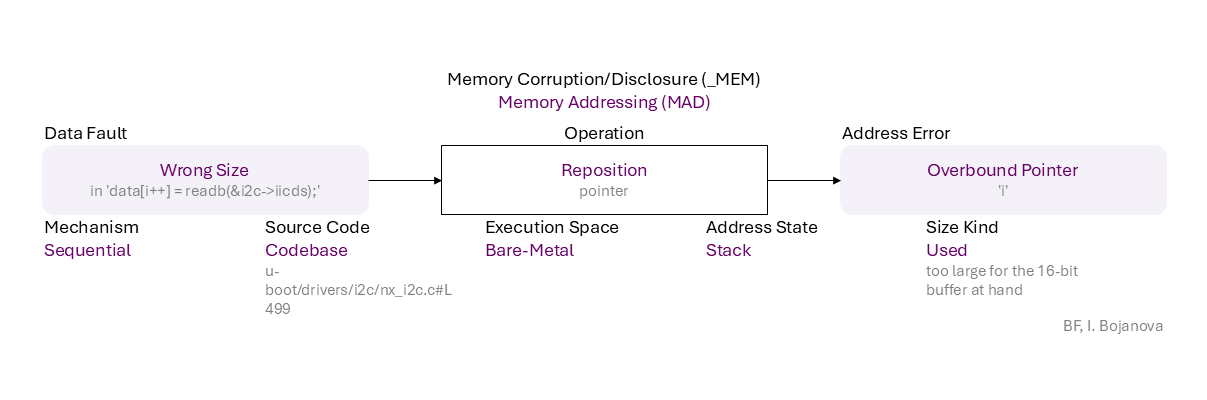
Wrong Size (in 'data[i++] = readb(&i2c->iicds);') to Reposition (pointer) on Stack with Used size (too large for the 16-bit buffer at hand) using Sequential mechanism in Codebase source code (u-boot/drivers/i2c/nx_i2c.c#L499) in Bare-Metal execution space that results in Overbound Pointer ('i') error, which propagates to
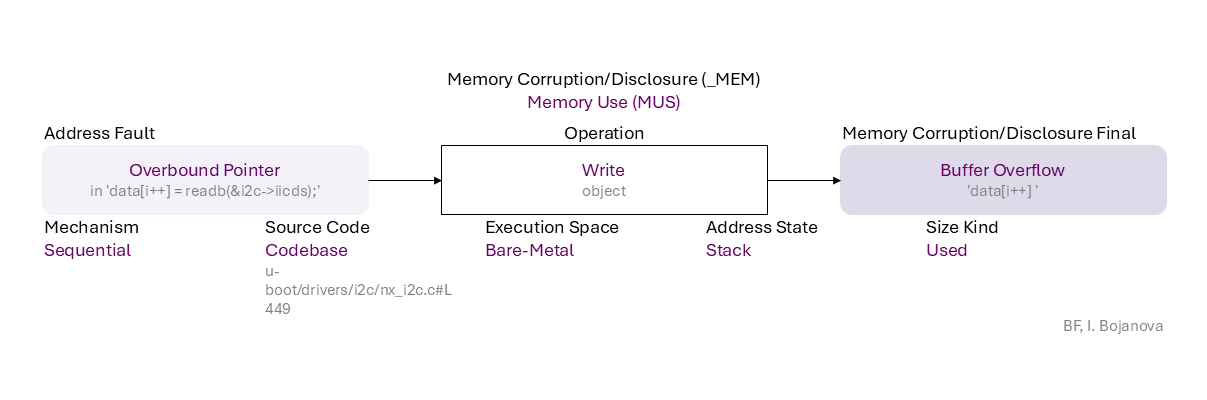
Overbound Pointer (in 'data[i++] = readb(&i2c->iicds);') to Write (object) on Stack with Used size using Sequential mechanism in Codebase source code (u-boot/drivers/i2c/nx_i2c.c#L449) in Bare-Metal execution space that results in Buffer Overflow ('data[i++] ') final error, which can be exploited toward
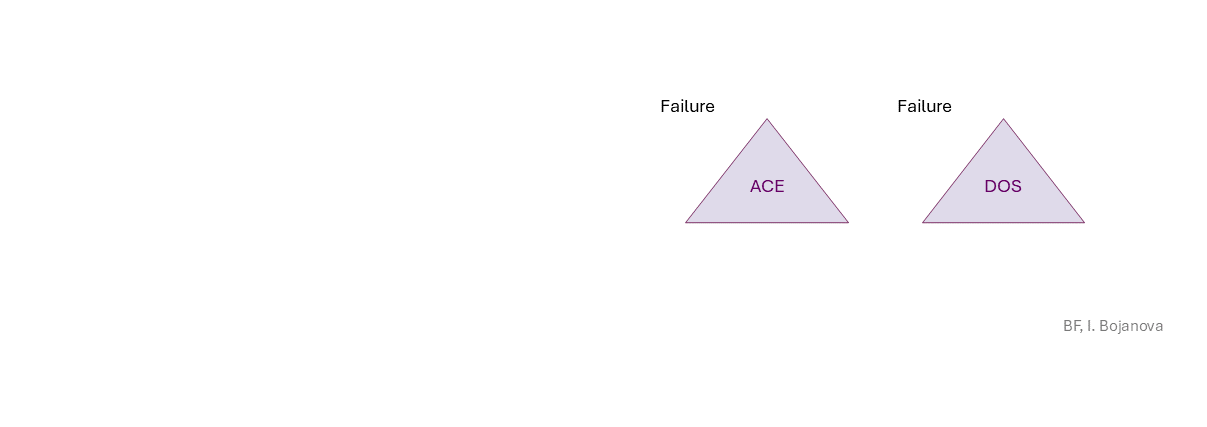
Arbitrary Code Execution (ACE) (everything could be lost),Denial of Service (DOS) (availability loss) security failure.
|
| Class | Definition |
| DCL | Declaration (DCL) class – An object, a function, a type, or a namespace is declared or defined improperly. |
| TCV | Type Conversion (TCV) class – Data are converted or coerced into other type improperly. |
| TCM | Type Computation (TCM) class – An arithmetic expression (over numbers, strings, or pointers) is calculated improperly, or a boolean condition is evaluated improperly. |
| MAD | Memory Addressing (MAD) class – The pointer to an object is initialized, dereferenced, repositioned, or reassigned to an improper memory address. |
| MUS | Memory Use (MUS) class – An object is initialized, read, written, or cleared improperly. |
| Operation | Definition |
| Declare | Declare operation – Specify the name and type of an object; the name, return type, and parameters of a function; or the name and type parameters of a type. |
| Coerce | Coerce operation – Implicitly (forced by the Type System) convert the value of a passed in/out argument or the return into the corresponding parameter or return data type. (Type Coercion is known also as Type Juggling.) |
| Evaluate | Evaluate operation – Find the result of a Boolean condition (incl. comparison). |
| Reposition | Reposition operation – Change the pointer to another position inside its object. |
| Write | Write operation – Change the data value of an object in memory to another meaningful value. |
| Cause/Consequence | Definition |
| Code Bug | Code Bug type – An error in the implementation of an operation – proper operands over an improper operation. It is the roor cause of a security vulnerability. Must be fixed to resolve the vulnerability. |
| Erroneous Code | Erroneous Code bug - There is a coding error in the implementation of the operation. |
| Type | Type error (or fault) type – The set or range of allowed values of an entity is wrong or the operations allowed on them are wrong. |
| Wrong Type | Wrong Type error (or fault) – A data type range or structure is not correct. |
| Data Error/Fault | Data error (or fault) type – The data of an object has harmed semantics or inconsistent or wrong value. |
| Flipped Sign | Flipped Sign error (or fault) – Sign bit is overwritten from type related calculation. |
| Wrong Argument | Wrong Argument error (or fault) – Inaccurate input data value, i.e., non-verified for harmed semantics. |
| Under Range | Under Range error (or fault) – The data value is smaller than the lower range of its type. |
| Truncated Value | Truncated Value error (or fault) – The rightmost bits of a data value that won’t fit the data type size are cut off. |
| Wrong Size | Wrong Size error (or fault) – The value used as size or length (i.e., the number of elements) does not match the object's memory size or length (e.g., to limit a pointer reposition or index increment/decrement in a repetition statement). |
| Address Error/Fault | Address error (or fault) type – The address of an object is wrong. |
| Overbound Pointer | Overbound Pointer error (or fault) – Holds an address that is above the upper boundary of its object. |
| Memory Corruption/Disclosure Final Error | Memory Corruption/Disclosure final error/exploit vector type – An exploitable or undefined system behavior caused by memory addressing, allocation, use, or deallocation bugs. |
| Buffer Overflow | Buffer Overflow final error – Write data above the upper bound of an object (i.e., buffer over-write). |
| Operation Attribute | Definition |
| Mechanism | Mechanism operation attribute type – Shows how the operation with a bug or faulty operand is performed. |
| Simple | Simple operation attribute – The operation is via non-polymorphic types. |
| Pass Out | Pass Out operation attribute – The operation is via out or in/out arguments' values or a return value to a function/ operator. |
| Operator | Operator operation attribute – The operation is via a function with a symbolic name that implements a mathematical, relational or logical operation. |
| Pass In | Pass In operation attribute – The operation is via in arguments' values to a function/ operator. |
| Sequential | Sequential operation attribute – The operation is via iterating over the object elements. |
| Source Code | Source Code operation attribute type – Shows where the code of the operation with a bug or faulty operand resides within the software, firmware, or hardware. |
| Codebase | Codebase operation attribute – The operation is in the programmer's code - in the application itself. |
| Execution Space | Execution Space operation attribute type – Shows where the operation with a bug or faulty operand is executed and the privilege level at which it runs. |
| Bare-Metal | Bare-Metal operation attribute – The bugged code runs in an environment without privilege control. Usually, the program is the only software running and has total access to the hardware. |
| Operand Attribute | Definition |
| Name Kind | Name Kind operand attribute type – Shows what the entity with this name is. |
| Object | Object operand attribute – A memory region used to store data. |
| Type Kind | Type Kind operand attribute type – Shows what the data type composition is. |
| Primitive | Primitive operand attribute – A scalar data type that mimics the hardware units - e.g., int (long, short, signed), float, double, string, Boolean. A primitive data type is only language defined and is not built from other data types. |
| Name State | Name State operand attribute type – Shows what the stage of the entity name is. |
| Resolved | Resolved operand attribute – The name scope is known to the Type System. |
| Data Kind | Data Kind operand attribute type – Shows what the type or category of data is. |
| Numeric | Numeric operand attribute – A number – a sequence of digits. |
| Address State | Address State operand attribute type – Shows where the address is (i.e., its location) in the memory layout. |
| Stack | The object is a non-static local variable (defined in a function, a passed parameter, or a function return address). |
| Size Kind | Size Kind operand attribute type – Shows what is used as the size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of an object - e.g., as the limit for traversal over the elements. |
| Used | Used operand attribute – A supplied value to be used as the size or length (i.e., the number of elements) of an object. |
| Failure | Definition |
| ACE | Arbitrary Code Execution (ACE) – Execution of unauthorized commands or code execution that could lead to everything being lost; remote code execution (RCE) is a sub-case of ACE on a target system or device from a remote location, typically over a network. |
| DOS | Denial of Service (DOS) – Disruption of access to or use of information or information systems that leads to availability loss. |